Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What happens when a ray of light falls normally (or perpendiculary) on the surface of a plane mirror?
Solution
When a ray of light falls normally (or perpendicularly) on the surface of a plane mirror, it gets reflected along the same path because the angles of incidence and reflection are both equal to zero.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is a virtual image?
A ray of light is incident on a plane mirror at an angle of 30°. What is the angle of reflection
The letter F is placed in front of a plane mirror:
What is the name of the phenomenon involved?
What do you mean by the term dispersion?
A student obtained on a screen the sharp image of a candle flame placed at the farther end of laboratory table using a concave mirror. For getting better value of focal length of the mirror, the teacher suggested to him to focus the sun. What should the student do?
(A) Should move the mirror away from the screen.
(B) Should move the mirror towards the screen.
(C) Should move the mirror and screen both towards the sun.
(D) Should move only the screen towards the sun.
Define the following term in relation to concave mirror.
Principal axis
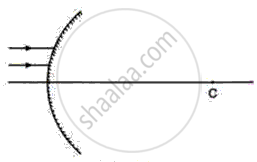
The diagram below shows the parallel rays incident on a convex mirror. C is the centre of the curvature of the mirror. By drawing the paths of the reflected rays, label the focus F and hence find the focal length of the mirror.
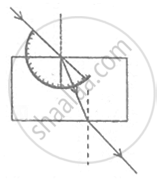
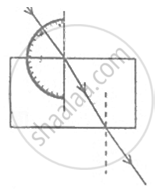
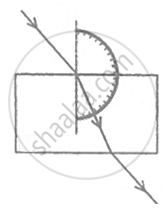
A student traces the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular slab.
 |
 |
 |
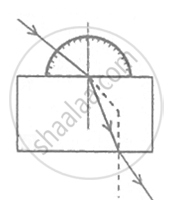 |
For measuring the angle of incidence, he must position the protractor in the manner shown in the figure:
Explain why a ray of light passing through the center of curvature of a concave mirror, gets reflected along with the same pattern.
