Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
What is biological magnification?
What is meant by biological magnification?
Solution 1
Biological magnification is defined as the phenomenon of the accumulation or increase in the concentration of some toxic substances at each trophic level.
Solution 2
A progressive increase in the concentration of non-biodegradable substances in a food chain is called biological magnification.
Solution 3
The increase in the concentration of harmful substances, such as pesticides, in the bodies of living organisms at each level of a food chain is called biological magnification.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The first trophic level in a food chain is always a green plant. Why ?
We do not clean natural ponds or lakes but an aquarium needs to be cleaned regularly. Why is it so ? Explain.
Will the impact of removing all the organisms in a trophic level be different for different trophic levels? Can the organisms of any trophic level be removed without causing any damage to the ecosystem?
The following statement is true or false :
Secondary consumers and tertiary consumers, both are carnivores.
Which of the following belong to the same trophic level?
Tree ; Frog ; Snake ; Grass ; Lizard
Which organisms belong to third and fourth trophic levels in the food chain comprising the following?
Rats, Plants, Hawk, Snakes
Give an example of a four step food chain operating in grassland. Name the secondary consumer in this food chain
At which trophic level a person is feeding when he is eating bread.
Give two differences between food chain and food web.
Which of the following are decomposers of dead organisms?
| Bacteria | Fungi | Viruses |
| (a) no | yes | yes |
| (b) yes | no | yes |
| (c) yes | yes | no |
| (d) yes | yes | yes |
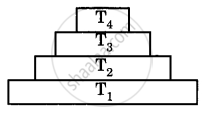
In the figure given alongside, the various trophic levels are shown in the form of a pyramid. At which trophic level the maximum energy is available?
A food chain occurring in the sea which provides food for many people can be written as :
phytoplankton → zooplankton → X → Y
What could be X?
In a food chain consisting of grass, frog, bird and insects, where will the concentration of the harmful chemicals be maximum?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
Grass → ........... → Human
What is ten per cent law? Explain with an example.
How much energy will be available to hawks in the food chain comprising hawk, snake, paddy and mice, if 10,000 J of energy is available to paddy from the sun?
If the energy available at the producer level in a food chain is 150 J, how much energy will be transferred to : tertiary consumer?
(a) 15 J
(b) 10 J
(c) 1.50 J
(d) 0.15 J
Answer the following question.
Human body is made up of five important components, of which water is the main component. Food, as well as potable water, are essential for every human being. The food is obtained from plants through agriculture. Pesticides are being used extensively for a high yield in the fields. These pesticides are absorbed by the plants from the soil along with water and minerals and from the water bodies, these pesticides are taken up by the aquatic animals and plants. As these chemicals are not biodegradables, they get accumulated progressively at each trophic level. The maximum concentration of these chemicals gets accumulated in our bodies and greatly affects the health of our mind and body.
(a) Why is the maximum concentration of pesticides found in human beings?
(b) Give one method which could be applied to reduce our intake of pesticides through food to some extent.
(c) Various steps in a food chain represent :
(a) Food web
(b) Trophic level
(c) Ecosystem
(d) Biomagnification
(d) With regard to various food chains operating in an ecosystem, man is a:
(a) Consumer
(b) Producer
(c) Producer and consumer
(d) Producer and decomposer
Give some examples for Biodegradable and Non-biodegradable waste.
| S. No. | Biodegradable waste | Non-biodegradable waste |
| 1. | Food Waste | Plastic Bottles |
| 2. | ||
| 3. | ||
| 4. | ||
| 5. |
