Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is a dihybrid cross? How did Mendel perform this cross?
Solution
Dihybrid Cross: A cross between two parents taking into consideration alternative traits of two different characters. For example, a cross between a round and yellow seed-bearing plant with wrinkled and green seed-bearing plant.

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Two heterozygous parents are crossed. If the two loci are linked what would be the distribution of phenotypic features in F1 generation for a dihybrid cross?
Multiple Choice Question
When two individuals differing in at least one character are crossed, the process is known as:
Under which conditions does the law of independent assortment hold good and why?
The genotype of a plant showing the dominant phenotype can be determined by
What is back cross?
What are the reasons for Mendel’s successes in his breeding experiment?
Explain the law of dominance in a monohybrid cross.
Identify the statementls that is/are NOT the correct reason/s for Mendel's success in his hybridization experiments.
i. Each factor controlled the single trait and is located on separate chromosomes.
ii. In the pea plant, contrasting characters can be easily recognized.
iii. Mendel carefully recorded the number of plants of each type and expressed his results as ratios.
iv. Mendel performed biochemical assays for identifying the position of 'factors' on chromosome.
In a dihybrid cross, if you get 9:3:3:1 ratio it denotes that ______.
In a testcross involving F1 dihybrid flies, more parental-type offspring were produced than the recombinant-type offspring. This indicates ______.
Two linked genes a and b show 20% recombination. The individuals of a dihybrid cross between ++ /++ × ab/ab shall show gametes ______.
A dihybrid condition is ______.
Mendel’s last law is ______.
Given below is a dihybrid cross performed on Drosophila.
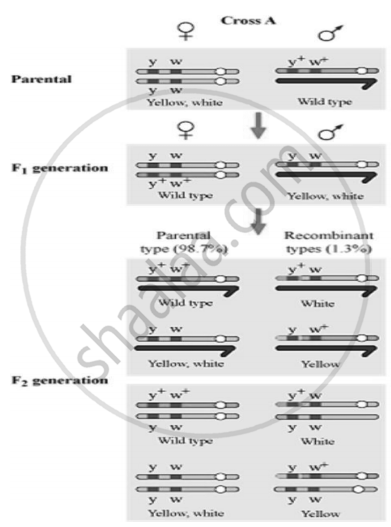
Which of the following conclusions can be drawn on the basis of this cross? When yellow bodied (y), white-eyed (w) Drosophila females were hybridized with brown bodied (y+), red-eyed males (w+) and F1 progenies were intercrossed, F2 generation would have shown the following ratio:
What is the difference between genetic drift and change due to natural selection?
How is the sex of a newborn determined in humans?
Do genetic combination of mothers play a significant role in determining the sex of a new born?
Which of the following statement is not correct for two genes that show 50% recombination frequency?
The Law of independent assortment is applicable for the traits which ______
