Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is heat? What is the S. I. unit of heat?
Solution
Heat is a form of energy, which when absorbed by a body makes it hot and when extracted from a makes it cold. It is also defined as the total kinetic energy possessed by all the molecules of a body. The S. I. unit of heat is joule/kg kelvin.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What impact will global warming have on the health of the affected population?
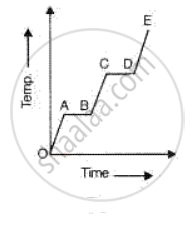
A substance is heated at a constant rate from a low temperature to a high temperature. A graph of temperature against time is shown in the figure. Which part or parts of the graph correspond(s) to the substance existing in two states?
If substances A and B are liquids then which one would be more useful in car radiators?
Given: Specific heat capacity’A’ 3.8 J/g /K. Specific heat capacity ‘B’ 0.4 J/g /K.
Will the value of specific heat’capacity and specific latent heat of a substance change if the scale is °F instead of °C?
Read the passage and answer the questions based on it.
If heat is exchanged between a hot and cold object, the temperature of the cold object goes on increasing due to gain of energy and the temperature of the hot object goes on decreasing due to loss of energy. The change in temperature continues till the temperatures of both objects attain the same value. In this process, the cold object gains heat energy and the hot object loses heat energy. If the system of both the objects is isolated from the environment by keeping it inside a heat-resistant box then no energy can flow from inside the box or come into the box. In this situation, we get the following principle.
Heat energy lost by the hot object = Heat energy gained by the cold object. This is called the ‘Principle of heat exchange’.
- Where does heat transfer take place?
- In such a situation which principle of heat do you perceive?
- How can this principle be explained in short?
- Which property of the substance is measured using this principle?
Two uniform brass rods A and B of length land 2l and radii 2r and r respectively are heated to the same temperature. The ratio of the increase in the volume ofB to that of A is ____________.
A monoatomic gas of pressure 'P' having volume 'V' expands isothermally to a volume '2V' and then adiabatically to a volume '16V'. The final pressure of the gas is ______.
(ratio of specific heats = `5/3`)
