Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is the work done by the force of gravity on a satellite moving round the earth? Justify your answer.
Solution
When a satellite orbits the earth, its displacement over a short period of time is along the tangent to the satellite's circular route. The gravitational force (F) exerted on the satellite due to the earth is along the radius depicted in the picture.
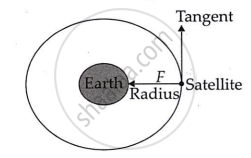
Because a tangent is always perpendicular to the radius, both displacement and force are perpendicular. The satellite experiences no displacement in the direction of the force, i.e., s = 0. As a result, the force of gravity on the satellite produces no work since W = F × s = 0.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A load of 100 kg is pulled up by 5 m. Calculate the work done. (g = 9.8 m/s2)
Calculate the work done by the brakes of a car of mass 1000 kg when its speed is reduced from 20 m/s to 10 m/s?
A body of mass 100 kg is lifted up by 10 m. Find :
(i) the amount of work done
(ii) potential energy of the body at that height (value of g = 10 m/s2)
A trolley is pushed along a road with a force of 400 N through a distance of 60 m in 1 minute. Calculate the power developed.
An electric heater uses 600 kJ of electrical energy in 5 minutes. Calculate its power rating.
A car of weight 20000 N climbs up a hill at a steady speed of 8 m/s, gaining a height of 120 m is 100 s. Calculate : work done by the car.
Define power. Give the SI unit of power.
In loading a truck, a man lifts boxes of 100 N each through a height of 1.5 m.
How much work does he do in lifting one box?
In loading a truck, a man lifts boxes of 100 N each through a height of 1.5 m.
If the man lifts 4 boxes per minute, at what power is he working?
(g = 10 m s−2)
How is the power related to the speed at which a body can be lifted? How many kilograms will a man working at the power of 100 W, be able to lift at a constant speed of 1 m s–1 vertically? (g = 10 m s–2)
