Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What kind of change takes place in a nucleus when a β - particle is emitted? Express it by an equation. State whether
- atomic number and
- mass number are conserved in a radioactive β - decay?
Solution
On emitting a β particle, the number of nucleons in the nucleus (i.e. protons and neutrons) remains same, but the number of neutrons is decreased by one and the number of protons is increased by one.
If a radioactive nucleus P with mass number A and atomic number Z emits a beta particle to form a daughter nucleus Q with mass number A and atomic number Z+1, then the change can be represented as follows:
\[\ce{\underset{Parent nucleus}{^A_Z P} ->[β particle]} \] \[\ce{\underset{Daughter nucleus}{{^A_{z+1} Q}}} + \underset{\ce{(Beta-particle)}}{{^0_{-1} e}}\]
- Atomic number 'Z' is not conserved. It is increased by 1.
- Mass number A is conserved.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What happens to the position of an element in the periodic table when its nucleus emits β -particle? Give reasons for your answer.
A nucleus is \[\ce {^24_11 Na} \] β-radioactive.
What general name is given to the product nucleus with respect to \[\ce{^24_11 Na}\]?
In β-emission from a radioactive substance, an electron is ejected. This electron comes from ______.
Define critical mass.
A radioactive nucleus containing 128 nucleons emits a β-particle. After β- emission the number of nucleons present in the nucleus will be ______.
|
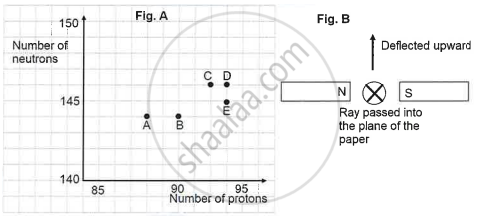
The graph (fig A) illustrates the correlation between the number of protons (x-axis) and the number of neutrons (y-axis) for elements A, B, C, D, and E in the periodic table. These elements are denoted by the letters rather than their conventional symbols. When the element C, depicted in the graph, undergoes radioactive decay, it releases radioactive rays. When these rays are directed into the plane of the paper in the presence of a magnetic field, as indicated in the fig B, they experience deflection, causing them to move upwards.
|
Name the radioactive radiations emitted by the element C.
|
The graph (fig A) illustrates the correlation between the number of protons (x-axis) and the number of neutrons (y-axis) for elements A, B, C, D, and E in the periodic table. These elements are denoted by the letters rather than their conventional symbols. When the element C, depicted in the graph, undergoes radioactive decay, it releases radioactive rays. When these rays are directed into the plane of the paper in the presence of a magnetic field, as indicated in the fig B, they experience deflection, causing them to move upwards.
|
Identify the daughter element from the graph.
When happens to the (i) atomic number, (ii) mass number of the nucleus of an element when a β-particle is emitted ?
What changes occur in the nucleus of a radioactive element when it emits a beta particle. Give one example, in support of your answer.
A nucleus \[\ce{^24_11Na}\] is β-radioactive.
Write the equation representing β-decay.