Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
(a) What is the largest average velocity of blood flow in an artery of radius 2 × 10–3 m if the flow must remain laminar? (b) What is the corresponding flow rate? (Take viscosity of blood to be 2.084 × 10–3 Pa s).
Solution 1
a)
Radius of the artery, r = 2 × 10–3 m
Diameter of the artery, d = 2 × 2 × 10–3 m = 4 × 10– 3 m
Viscosity of blood, eta = `2.084 xx 10^(-3)` Pas
Density of blood, ρ = 1.06 × 103 kg/m3
Reynolds’ number for laminar flow, NR = 2000
The largest average velocity of blood is given by the relation:
`V_"arg" = (N_Reta)/(rhod)`
= `(2000xx2.084xx10^(-3))/(1.06xx10^3xx4xx10^(-3))`
= 0.983 m/s
Therefore, the largest average velocity of blood is 0.983 m/s.
b) Flow rate is given by the relation:
`R = pir^2V_"arg"`
`= 3.14 xx (2xx10^(-3))^2 xx 0.983`
`= 1.235 xx 10^(-5) m^3 s^(-1)`
Therefore, the corresponding flow rate is `1.235 xx 10^(-5) m^3 s^(-1)`
Solution 2
Here `r = 2 xx 10^(-3) m; D = 2r = 2xx2xx10^(-3) = 4xx 10^(-3) m`
`eta = 2.084 xx 10^(-3) Pa-s; rho = 1.06 xx 10^3 kg m^(-3)`
For flow to be laminar , `N_R = 2000`
a) Now `v_c = `(N_Reta)/rho_D` = (2000xx(2.084xx10^(-3)))/((1.06xx10^3)xx(4xx10^(-3))) = 0.98 "m/s"`
b)Volume flowering per second =`pir^2v_c = 22/7 xx (2xx10^(-3))^2 xx 0.98 = 1.23 xx 10^(-5) m^3s^(-1)`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In Millikan’s oil drop experiment, what is the terminal speed of an uncharged drop of radius 2.0 × 10–5 m and density 1.2 × 103 kg m–3? Take the viscosity of air at the temperature of the experiment to be 1.8 × 10–5 Pa s. How much is the viscous force on the drop at that speed? Neglect buoyancy of the drop due to air.
The viscous force acting between two layers of a liquid is given by \[\frac{F}{A} = - \eta\frac{dv}{dz}\]. This F/A may be called
A raindrop falls near the surface of the earth with almost uniform velocity because
A spherical ball is dropped in a long column of a viscous liquid. The speed of the ball as a function of time may be best represented by the graph
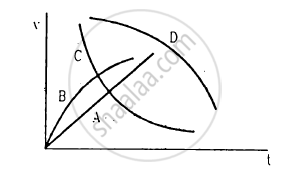
A small sphere of radius 2 cm falls from rest in a viscous liquid. Heat is produced due to viscous force. The rate of production of heat when the sphere attains its terminal velocity is proportional to
In a horizontal pipe of non-uniform cross-section, water flows with a velocity of 1 ms−1 at a point where the diameter of the pipe is 20 cm. The velocity of water (1.5 ms−1) at a point where the diameter of the pipe is (in cm)
A block of Ag of mass x kg hanging from a string is immersed in a liquid of relative density 0.72. If the relative density of Ag is 10 and tension in the string is 37.12 N then compute the mass of Ag block.
Why two holes are made to empty an oil tin?
The coefficient of apparent expansion of mercury in a glass vessel is 153 × 10-6/°C and in a steel vessel is 144 × 10-6/°C. If α for steel is 12 × 10-6/°C, then that of glass is ______.
A liquid of density ρ and coefficient of viscosity η flows with velocity v through a tube of diameter D. A quantity `"R" = (rho"vD")/η`, determines whether the flow will be streamlined or turbulent. R has the dimension of ______.
