Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
What is meant by inelastic demand?
Give the meaning of inelastic demand.
Solution
When a large change in the price does not bring so much change in the demand, the demand is said to be inelastic. In this situation, percentage change in demand is lesser than the percentage change in price.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Compare inelastic demand with perfectly inelastic demand.
Fill in the blank using proper alternative given in the bracket:
Perfectly inelastic demand curve is.....................................................
State with reason. Whether you ‘agree’ or ‘disagree’ with the following statement:
There are no exceptions to the law of Demand.
Fill in the blank with proper alternatives given in the bracket:
Indirect demand is also known as _______ demand.
Write whether the following statement is True or False:
Salt has elastic demand.
Define or explain the concept of Demand schedule.
Fill in the blank with appropriate alternatives given below:
When the price of petrol goes up, demand of cars will ___________.
Fill in the blank with appropriate alternatives given below:
Market demand is an aggregate of purchasing by _________ buyers.
Give reason or explain the following statement.
Demand curve slopes downward from left to right.
In case of ______ supply curve is a vertical straight line parallel to Y-axis.
There is a sudden change in climatic conditions resulting in hot weather. Assuming no change in the price of the cold drinks, it will lead to ______
If the increase in demand is greater than the increase in supply, then equilibrium price will ______
What will be the effect on equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity when income increases in case of normal goods?
Which of the following statements is correct with respect to the correction of Excess Demand?
Which of the following is correct?
If there is no change in the demand for commodity X, even after a rise in its price, then its demand is ______
Demand deposits include:
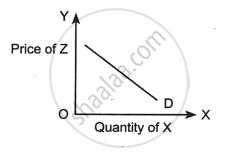
The figure given below shows the relation between the quantity demanded for the good X and the price of the good Z. What type of goods are X and Z?