Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is the range of vision of a normal human eye?
Solution
The range of vision of a normal human eye is from 25 cm (near point) to infinity (far point).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How does the eye adjust to take account of an increase in brightness?
Explain the functions of the following parts of the eye:
(i) cornea
(ii) iris
(iii) pupil
(iv) ciliary muscles
(v) eye-lens
The human eye possesses the power of accommodation. This is the power to:
(a) alter the diameter of the pupil as the intensity of light changes
(b) distinguish between lights of different colours
(c) focus on objects at different distances
(d) decide which of the two objects is closer.
Out of animals of prey and predators, which have their eyes:
at the front of their head?
In the figure of the human eye, the cornea is represented by the letter
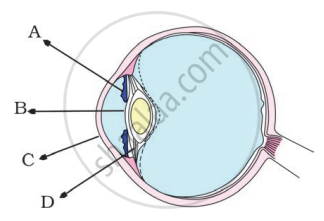
Name the part of the eye which gives colour to the eyes.
With reference to human eye, answer the following question.
What is blind spot?
| Column I | Column II | ||
| 1 | Retina | a | Path way of light |
| 2 | Pupil | b | Far point comes closer |
| 3 | Ciliary muscles | c | near point moves away |
| 4 | Myopia | d | Screen of the eye |
| 5 | Hypermetropia | e | Power of accomodation |
The thin, transparent extension of sclerotic layer found in front of the lens is ______.
Differentiate between members of the following pair with reference to what is asked in the bracket.
Aqueous humour and vitreous humour (location).
