Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What will be the pressure of the gaseous mixture when 0.5 L of H2 at 0.8 bar and 2.0 L of dioxygen at 0.7 bar are introduced in a 1L vessel at 27°C?
Solution 1
Calculation of partial pressure of H2 in 1L vessel P1= 0.8 bar,
P2= ? V1= 0.5 L , V2 = 1.0 L
As temperature remains constant,
P1V1 = P2V2
(0.8 bar) (0.5 L) = P2 (1.0 L) or
P2 = 0.40 bar, i.e., PH2 = 0.40 bar
Calculation of partial pressure of 02 in 1 L vessel
P1‘ V1 = P2‘V2‘
(0.7 bar) (2.0 L) = P2 (1L) or
P2‘ = 1.4 bar, i.e.,Po2= 1.4 bar
Total pressure =PHz + PQ2
= 0.4 bar + 1.4 bar
= 1.8 bar
Solution 2
Let the partial pressure of H2 in the vessel be `"P"_("H"_2)`
Now
`"p"_1 = 0.8 " bar"` `"p"_2 = "p"_("H"_2) = ?`
`"V"_1 = 0.5L "V"_2 = 1 "L"`
it is known that
`"p"_1"V"_1 = "p"_2"V"_2`
`=> "p"_2 = ("p"_1"V"_1)/"V"_2`
`=> "p"_("H"_2) = (0.8 xx 0.5)/1`
= 0.4 bar
Now, let the partial pressure of O2 in the vessel be `"po"_2`
Now,
`"p"_1` = 0.7 bar `"p"_2 = "po"_2 = ?`
`"V"_1` = 2.0 L `V_2 = 1 L`
`"p"_1"V"_1 = "p"_2"V"_2`
`⇒ "p"_2 = "p"_1"V"_1"V"_2`
`⇒ "pO"_2` = 0.7 × 2.01
= 1.4 bar
Total pressure of the gas mixture in the vessel can be obtained as:
`"p"_"total" = "p"_("H"_2) + "po"_2`
= 0.4 + 1.4
= 1.8 bar
Hence, the total pressure of the gaseous mixture in the vessel is 1.8 bar.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A vessel of 120 mL capacity contains a certain amount of gas at 35 °C and 1.2 bar pressure. The gas is transferred to another vessel of volume 180 mL at 35 °C. What would be its pressure?
Using the equation of state pV = nRT; show that at a given temperature density of a gas is proportional to gas pressure p.
Payload is defined as the difference between the mass of displaced air and the mass of the balloon. Calculate the payload when a balloon of radius 10 m, mass 100 kg is filled with helium at 1.66 bar at 27°C. (Density of air = 1.2 kg m–3 and R = 0.083 bar dm3 K–1 mol–1).
Gases deviate from ideal behavior at high pressure. Which of the following statement(s) is correct for non-ideality?
With regard to the gaseous state of matter which of the following statements are correct?
(i) Complete order of molecules
(ii) Complete disorder of molecules
(iii) Random motion of molecules
(iv) Fixed position of molecules
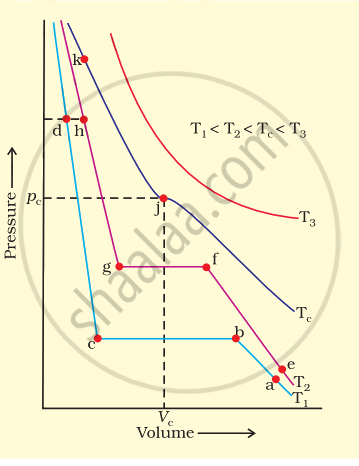
Isotherms of carbon dioxide at various temperatures are represented in figure. Answer the following questions based on this figure.
(i) In which state will \[\ce{CO2}\] exist between the points a and b at temperature T1?
(ii) At what point will \[\ce{CO2}\] start liquefying when temperature is T1?
(iii) At what point will \[\ce{CO2}\] be completely liquefied when temperature is T2.
(iv) Will condensation take place when the temperature is T3.
(v) What portion of the isotherm at T1 represent liquid and gaseous \[\ce{CO2}\] at equilibrium?