Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What will happen if microbes in the soil get destroyed?
Solution
Soil contains various kinds of microbes like bacteria, fungi, algae, protozoa, etc. All of these microorganisms play important roles like:
- Certain bacteria and blue-green algae have the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen. This, in turn, enriches the fertility of the soil. Such microorganisms are known as biological nitrogen fixers. Example: Rhizobium is a symbiotic bacteria that lives in the root nodules of leguminous plants. Rhizobium fixes atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogenous compounds.
- The bacteria and fungi present in soil decompose dead organic wastes of plants and animals and convert them into manure. The manure contributes to the humus content of the soil, thereby helping in increasing its fertility.
- Not only these, microorganisms that are found in soil are also a part of many biogeochemical cycles that would not take place in their absence.
The above points explain the fact that how important microbes are and if they are destroyed, their effect can be irreversible.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Why should the use of cattle cake as fuel be discouraged?
Multiple choice questions.
Which one of the following type of resource is iron ore?
Why should we use natural resources properly and judiciously? Explain your views.
Both ______ and ______ constituents are present in the soil.
Name the following.
Fossil fuel
Radon is used in decorative lights.
Describe natural resources with reference to the following:
Forest resources
How does the economic condition of a nation depend on its natural resources?
What is the use of the following resource?
Forests
What is the use of the following resource?
Animals
What is the use of the following resource?
Minerals
What is the use of the following resource?
Land
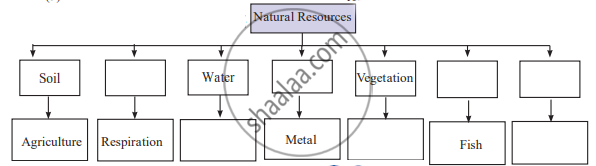
Complete the following flow chart.
Which products are obtained from forests?
What are the purposes for which land is used?
Man mined precious metals simultaneously for making ______.
The growth of Lichens on barren rocks is followed by the growth of
