Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
When a fork is seen through lenses A and B one by one, it appears as shown in the diagrams. What is the nature of (i) lens A, and (ii) lens B? Give reason for your answer.
Solution
When the fork is seen through lens A, it appears to be diminished. Such diminished object is observed when it is placed near a concave lens. Therefore, lens A is concave, i.e., diverging in nature.
When the fork is seen through lens B, it appears to be enlarged. Such enlarged image is formed by a convex lens when an object is placed between the lens and its focus. Therefore, lens B is a convex, i.e., converging in nature.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Where must the object be placed for the image formed by a converging lens to be:
real, inverted and larger than the object?
State whether concave lens has a real focus or a virtual focus.
If the image formed by a lens is always diminished and erect, what is the nature of the lens?
Take down this figure into your answer book and complete the path of the ray.
Give the position, size and nature of image of formed by a concave lens when the object is placed:
at infinity.
Out of the two lenses, one concave and the other convex, state which one will show the divergent action on a light beam. Draw diagrams to illustrate your answer.
Study the diagram below.
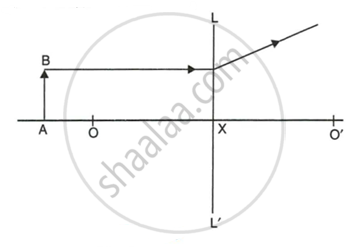
- Name the lens LL’.
- What are the points O and O' called ?
- Complete the diagram to form the image of the object AB.
- State three characteristics of the image.
A concave lens forms the image of an object which is ______.
A concave lens has a focal length 30 cm. Find the position and magnification (m) of the image for an object placed in front of it at distance 30 cm. State whether the image is real or virtual?
Convex magnifying glass is called divergent magnifying glass and concave magnifying glass is called converging magnifying glass.
