Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why does a current carrying, freely suspended solenoid rest along a particular direction?
Solution
A current-carrying freely suspended solenoid acts as a bar magnet, and thus, due to the Earth’s magnetic field, it rests along a particular direction.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The adjacent diagram shows a small magnet placed near a solenoid AB. Current is switched on in the solenoid by pressing the key K.
- State the polarity at the ends A and B.
- Will the magnet be attracted or repelled? Give a reason for your answer.

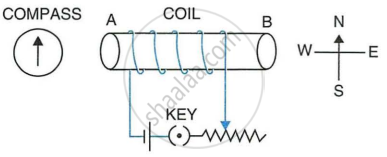
The following diagram shows a spiral coil wound on a hollow carboard tube AB. A magnetic compass is placed close to it. Current is switched on by closing the key.
- What will be the polarity at the ends A and B?
- How will the compass needle be affected? Give reason.
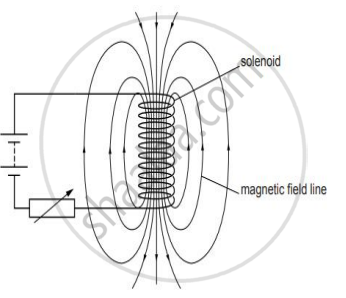
Draw the pattern of magnetic field lines of a solenoid through which a steady current flows. What does the pattern of field lines inside the solenoid indicate?
Derive the expression for the heat produced due to a current ‘I’ flowing for a time interval ‘t’ through a resistor ‘R’ having a potential difference ‘V’ across its ends. With which name is the relation known? How much heat will an instrument of 12W produce in one minute if it is connected to a battery of 12V?
Which of the following diagrams correctly shows the magnetic field produced by a current-carrying wire?
The factors on which one magnetic field strength is produced by current-carrying solenoids depends are
What does the divergence of magnetic field lines near the ends of a current carrying straight solenoid indicate?
The diagram below shows an insulated copper wire wound around a hollow cardboard cylindrical tube. Answer the questions that follow:
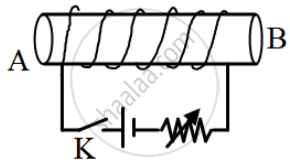
- What are the magnetic poles at A and B when the key K is closed?
- State two ways to increase the strength of the magnetic field in this coil without changing the coil.
- If we place a soft iron bar at the centre of the hollow cardboard and replace the DC source with an AC source then will it attract small iron pins toward itself when the current is flowing through the coil?
When does a solenoid behave as a magnet? Draw the pattern of the magnetic field produced inside it showing the directions of the magnetic field lines.
Refer to the image below and state how the magnetic field pattern indicates regions where the magnetic field is stronger outside the magnet. What happens to the magnetic field when the current in the circuit is reversed?