Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
With the help of a diagram, explain why the image of an object viewed through a concave lens appears smaller and closer than the object.
Solution
If we place an object anywhere between optical center and infinity, then the refraction occurs as in the below diagram:
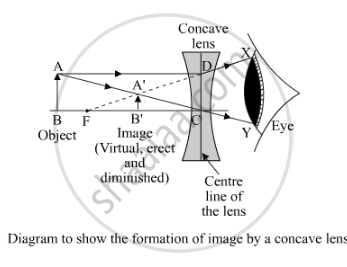
It is clear in the above ray diagram that the refracted rays meet a point within the focus. And also, this image virtual,erect and smaller than the object.
Thus, if an object is viewed through a concave lens, its image is appeared smaller and closer than the object.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When sunlight is concentrated on a piece of paper by a spherical mirror or lens, then a hole can be burnt in it. For doing this, the paper must be placed at he focus of:
(a) either a convex mirror or convex lens
(b) either a concave mirror or concave lens
(c) either a concave mirror or convex lens
(d) either a convex mirror or concave lens
A concave lens of focal length 15 cm forms an image 10 cm from the lens. How far is the object placed from the lens? Draw the ray diagram.
The power of a converging lens is 4.5 D and that of a diverging lens is 3 D. The power of this combination of lenses placed close together is :
(a) +1.5D
(b) +7.5D
(c) −7.5D
(d) −1.5D
What type of lens is used to correct
myopia?
A lens forms an upright and diminished image of an object irrespective of its position. What kind of lens is this?
An object is placed at a distance 24 cm in front of a convex lens of focal length 8 cm.
(i) What is the nature of the image so formed?
(ii) Calculate the distance of the image from the lens.
(iii) Calculate the magnification of the image.
Draw neat diagram to show the
Divergent action of concave lens
Distinguish between concave and convex lens.
An object is placed at a distance of 60 cm from a concave lens of focal length 30 cm.
(i) Use the lens formula to find the distance of the image from the lens.
(ii) List four characteristics of the image (nature, position, size, erect/inverted) formed by the lens in this case.
(iii) Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer of the part (ii).
Draw images in case of a concave lens when the object is at infinity.
