Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
With the help of a suitable diagram, discuss the relationship between Average product and Marginal Product.
Solution
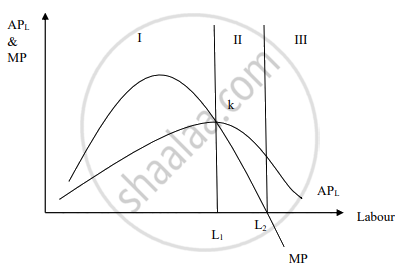
In Stage I (under the law of increasing return), when AP rises, MP > AP. The MP curve lies above the AP curve in the above diagram when it later slopes positively. At the end of stage I, when AP is at its maximum for L1 of labour, MP = AP and the MP curve intersects the AP curve at its maximum point, k.
In Stage II (under the law of diminishing return), when AP falls, MP < AP and the MP curve lies below the AP curve and intersects the labour axis, i.e., MP = 0, for the L2 level of labour at the end of Stage II.
In stage III (under the law of negative return), AP continues to fall but never becomes zero for positive labour. MP < 0 and the curve lies under the labour axis.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State the different phases of change in the total product according to the Law of Variable Proportions. Use diagram
What is the law of variable proportions?
Formula for calculating AP is
The short-run production is studied through
Mention the economies reaped from inside the firm
Product obtained from additional factors of production is termed as
Modern economists have propounded the law of
Bring out the Relationship among Total, Average and Marginal Products.
Which one of the following is NOT a ceteris paribus assumption of the Law of Supply?
Why is the AVC curve U-shaped?
At the point of inflexion, ______ is maximum.
Study the data given below and identify the laws followed in the production of A and B depicted in the Table I and Table II. Justify your answer with a reason for each.
| Table I | Table II | ||||
| Machines | Labour | Output of A (units) | Machines | Labour | Output of B (units) |
| 5 | 10 | 1000 | 5 | 10 | 400 |
| 5 | 11 | 1150 | 10 | 20 | 800 |
| 5 | 12 | 1310 | 15 | 30 | 1200 |
What are Average product?
What are Marginal product?
