Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
With the help of labelled diagram explain the exchange of gases between alveolus and capillary.
Solution

External respiration is the process of exchange of gases at the alveolar level. Alveoli consist of a layer of simple squamous epithelium resting on a basement membrane. They are intimately associated with a dense network of capillaries. The capillary wall is also made up of simple squamous epithelium resting on a thin basement membrane. Both the layers are thin walled and have similar structure. Together they form the respiratory membrane through which gaseous exchange occurs i.e. between the alveolar air and the blood. Diffusion of gases will take place from an area of higher partial pressure to an area of lower partial pressure until the partial pressure in the two regions reaches equilibrium. The partial pressure of CO2 of blood entering the pulmonary capillaries is 45 mmHg while partial pressure of CO2 in alveolar air is 40 mmHg.
This difference in partial pressure causes diffusion of CO2 from the capillaries into the alveolus. Similarly, partial pressure of O2 of blood in pulmonary capillaries is 40 mmHg while in alveolar air it is 104 mmHg. Due to this difference O2 diffuses from alveoli to the capillaries.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Answer briefly the following:
What is the difference between breathing and respiration?
How is the process of respiration different from breathing?
The volume of air that remains in the lungs after maximum respiration is ______.
Define Bohr effect and Haldane effect.
Which of the following is CORRECT with reference to oxygen dissociation curve?
Identify the role of NAD+ in cellular respiration
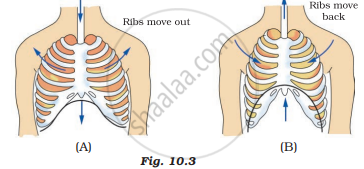
Observe the figures given in Figures 10.3 (A) and (B) and answer the following.
Which of the figures A or B indicates the process of inhalation and which is the process of exhalation?
In Hamburger’s phenomenon, ______.
What is oxygen dissociation curve?
Interpret the given diagrams A and B. Enlist the changes occuring, during inspiration and expiration.

