Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Write a note on sex linkage.
Solution
- Complete sex linkage:
a. It is exhibited by genes located on non-homologous regions of X and Y chromosomes.
b. They inherit together because crossing over does not occur in nonhomologous regions.
c. Examples of X-linked traits are haemophilia, red-green colour blindness, myopia (near sightedness) and for Y-linked are hypertrichosis, etc. - Incomplete sex linkage:
a. It is exhibited by genes located on homologous regions of X and Y chromosomes.
b. They do not inherit together because crossing over occurs in homologous regions.
c. Examples of X-Y linked traits are total colour blindness, nephritis, retinitis pigmentosa, etc.
RELATED QUESTIONS
How did Sturtevant explain gene mapping while working with Morgan?
British geneticist R.C. Punnett developed a graphical representation of a genetic cross called “Punnett Square”. Mention the possible result this representation predicts of the genetic cross carried.
Give detail account of sex-linked inheritance.
Which of the following refers to tendency of genes to inherit together?
The phenomenon of ____________ is universal and it is necessary for the natural selection, because it increases the chances of variation.
Linkage reduces the frequency of ______.
All genes located on the same chromosome ______.
A fruit fly heterozygous for sex-linked genes, is mated with normal female fruit fly. Male specific chromosome will enter egg cell in the proportion ______.
Genes located very close to one another on same chromosome tend to be transmitted together and are called as ______.
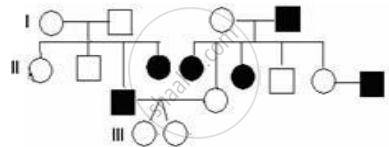
What is the pattern of inheritance in the above pedigree chart?