Commerce (English Medium)
Arts (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2022-2023
Date & Time: 17th March 2023, 10:30 am
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS :
- This question paper contains 34 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- This question paper contains two sections:
Section A – Macro Economics
Section B – Indian Economic Development - This paper contains 20 Multiple Choice Questions type questions of 1 mark each.
- This paper contains 4 Short Answer Questions type - I questions of 3 marks each to be answered in 60 to 80 words.
- This paper contains 6 Short Answer Questions type - II questions of 4 marks each to be answered in 80 to 100 words.
- This paper contains 4 Long Answer Questions type questions of 6 marks each to be answered in 100 to 150 words.
- Attempt all parts of questions together.
"In the Annual Budget 2022-23, the Government of India set up disinvestment targets of ₹ 65,000 crore".
Such proceeds from disinvestment can be classified as ______ receipts in the Government Budget as it leads to ______ of the Government.
capital, decrease in assets
revenue, increase in assets
capital, increase in liabilities
revenue, decrease in liabilities
Chapter: [0.05] Government Budget and the Economy
Assertion (A): The Balance of payments is in surplus, if autonomous receipts are greater than autonomous payments.
Reason (R): Autonomous transactions are determined by the difference in the Balance of Payments.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter: [0.06] Open Economy Macroeconomics
Read the following statements carefully:
Statement 1: The induced consumption shows, the direct relation between consumption and income.
Statement 2: With a certain increase in income, induced consumption also increases.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative from the following:
Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
Statement 1 is false and Statement 2 is true.
Both Statements 1 and 2 are true.
Both Statements 1 and 2 are false.
Chapter: [0.04] Determination of Income and Employment
Ms. lqra Ansari, a teacher, was explaining in her class about various types of deposits with the commercial banks. She quoted that - "These deposits form a part of M1 measure of money supply and are payable on demand by the commercial banks."
Identify the type of deposits she was explaining about and choose the correct alternative:
- Demand Deposits
- Time Deposits
- Post Office Deposits
Only (i)
(i) and (ii)
Only (ii)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
Chapter: [0.03] Money and Banking
As per the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) press report, dated 22nd June, 2022:
"Net Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI) recorded an outflow of US $15.2 billion mainly from the equity market."
The above transaction will be recorded in the ______ account on ______ side of Balance of payments account of India.
current, credit
capital, credit
current, debit
capital, debit
Chapter: [0.06] Open Economy Macroeconomics
Read the following statements carefully:
Statement 1: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the sum total of the gross market value of all the final goods and services added by all the sectors in the economy during a fiscal year.
Statement 2: Gross Value Added at Market Price (GVAMP) is equal to the excess of value of output over intermediate consumption.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
Statement 1 is false and Statement 2 is true.
Both Statements 1 and 2 are true.
Both Statements 1 and 2 are false.
Chapter: [0.02] National Income and Related Aggregates
On the basis of the figure given below, identify the type of flow indicated by B and D:
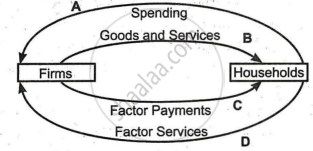
Real flow
Money flow
Nominal flow
National flow
Chapter: [0.02] National Income and Related Aggregates
Assuming that, the following data is given for an imaginary economy:
| Year → | 2020 (₹ in Cr.) |
2021 (₹ in Cr.) |
| Items ↓ | ||
| Exports of visibles | 1,000 | 1,100 |
| Imports of visibles | 800 | 850 |
The balance of Trade from 2020 to 2021 ______ by ₹ ______ crore.
increased, 200
increased, 50
decreased, 200
decreased, 50
Chapter: [0.06] Open Economy Macroeconomics
In order to tackle the problem of rising general price in an economy, government may come up with a surplus budget to achieve the budget objective of ______.
- reallocation of resources
- price stability
- redistribution of income
(i) only
(ii) only
(iii) only
(i) and (iii)
Chapter: [0.05] Government Budget and the Economy
Assertion (A): At the break-even level of income, the value of Average Propensity to Consume (APC) is zero.
Reason (R): Sum of Average Propensity to Consume (APC) and Average Propensity to Save (APS) is always equal to one.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter: [0.04] Determination of Income and Employment
______ refers to that level of Aggregate Demand, which can be met by the corresponding supply in the economy.
Autonomous Consumption
Effective Demand
Excess Demand
Deficient Demand
Chapter: [0.04] Determination of Income and Employment
In the Indian economy, ______ are issued by the Reserve Bank of India and acts as legal tender money.
- Coins of all denomination
- Currency notes of various denominations, except one rupee note
- Demand deposits
Only (i)
Only (ii)
Only (iii)
(i) and (ii)
Chapter: [0.03] Money and Banking
______ formulates the Monetary Policy in the economy.
Commercial Banks
International Monetary Fund
Central Bank
Central Government
Chapter: [0.03] Money and Banking
On the basis of the data given below for an imaginary economy, estimate the value of Net Domestic Product at factor cost (NDPFC):
| S.No. | Items | Amount (₹ in crore) |
| (i) | Household Consumption Expenditure | 2,000 |
| (ii) | Government Final Consumption Expenditure | 1,500 |
| (iii) | Gross Domestic Fixed Capital Formation | 1,000 |
| (iv) | Net additions to stock | 300 |
| (v) | Exports | 700 |
| (vi) | Net Indirect Taxes | 350 |
| (vii) | Imports | 200 |
| (viii) | Consumption of Fixed Capital | 250 |
Chapter: [0.02] National Income and Related Aggregates
On the basis of the data given below for an imaginary economy, estimate the Gross National Product at Market price (GNPMP):
| S.NO | Items | Amount (₹ in crore) |
| (i) | Household Consumption Expenditure | 2,000 |
| (ii) | Government Final Consumption Expenditure | 1,000 |
| (iii) | Gross Fixed Capital Formation | 1,100 |
| (iv) | Net additions to Stock | 200 |
| (v) | Exports | 600 |
| (vi) | Net factor income from abroad | 150 |
| (vii) | Imports | 400 |
Chapter: [0.02] National Income and Related Aggregates
''The process of credit creation by commercial banks comes to an end when the total of required reserves become equal to the initial deposits."
With the help of a numerical example, prove that the given statement is true.
Chapter: [0.03] Money and Banking
"In an economy ex-ante Aggregate Demand is more than ex-ante Aggregate Supply."
Explain its impact on the level of output, income and employment.
Chapter: [0.04] Determination of Income and Employment
Advertisements
“In an economy Planned spending is more than Planned output”.
Explain its impact on the level of output, income and employment.
Chapter: [0.04] Determination of Income and Employment
For a hypothetical economy, assuming there is an increase in the Marginal Propensity to Consume from 80% to 90% and change in investment to be ₹ 2000 crore.
Using the concept of investment multiplier, calculate the increase in income due to change in Marginal Propensity to Consume.
Chapter: [0.04] Determination of Income and Employment
"Many goods and services which may contribute to welfare, but are not included in estimating Gross Domestic Product (GDP)."
Do you agree with the given statement? Give valid reason in support of your answer.
Chapter: [0.02] National Income and Related Aggregates
Distinguish between final goods and intermediate goods. Give an example of each.
Chapter: [0.02] National Income and Related Aggregates
Distinguish between Real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and Nominal Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
Chapter: [0.02] National Income and Related Aggregates
State the meaning of 'normal resident' of a country.
Chapter: [0.02] National Income and Related Aggregates
Read the following text carefully. Answer the given questions on the basis of the same and common understanding:
| On 30th September 2022, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) raised Repo Rate for the fourth time in a row. The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) decided to raise the policy rate by 50 basis points `(1 "basis point" =1/100 "th of a percent")`. After this announcement, the new repo rate stands at 5.9%, while the reverse repo rate continues to stand at 3.35%. Commercial banks borrow money from the Central Bank, when there is a shortage of funds. With the surge in the repo rate, borrowings by general public will become costlier. This is because, as RBI hikes its repo rate, it becomes costly for the banks to borrow short term funds from the Central Bank.
As a result, the banks hike the rates at which customers borrow money from them to compensate for the hike in the repo rate. This happens because banks offer loans to retail consumers at an interest rate which is generally, directly proportional to the repo rate. The increase of 0.50 percent in repo rate will lead. to a higher interest rates on loans for borrowers, implying that the Equated Monthly Instalments (EMIS) for repaying the existing loans will also increase. |
- Differentiate between repo rate and reverse repo rate.
- Outline and discuss the measure taken by the Monetary Policy Committee of Reserve Bank of India to control inflation.
Chapter: [0.03] Money and Banking
Which of the following is NOT true about foreign trade during the colonial rule?
India suffered from a large trade deficit.
Restrictive policies of commodity production, were followed.
Britain maintained a monopoly control over lndia's exports and imports.
India became an exporter of primary products and an importer of finished consumer goods.
Chapter: [0.01] Indian Economy on the Eve of Independence
______ is a process, which includes all the activities from sowing till sale of the final produce in the market.
Rural Development
Agricultural Diversification
Organic Farming
Agricultural Marketing
Chapter: [0.06] Rural Development
______ have emerged as an important micro finance system and led to women empowerment.
NABARD
Self-Help Groups
Commercial Banks
Land Development Banks
Chapter: [0.06] Rural Development
Assertion (A): Human capital is not traded in the market; however its services are traded.
Reason (R): Human capital is intangible in nature.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter: [0.05] Human Capital Formation in India
Benefits of physical capital accrue only to private entities, whereas human capital provides private as well as ______ benefits.
profitable
fiscal
social
monetary
Chapter: [0.05] Human Capital Formation in India
Statement 1: China introduced structural economic reforms on its own, without any pressure.
Statement 2: Scholars argue that in India, the economic reforms process led to the worsening of all the economic indicators.
Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
Statement 1 is false and Statement 2 is true.
Both Statements 1 and 2 are true.
Both Statement 1 and 2 are false.
Chapter: [0.03] Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation : an Appraisal
Which of the following was NOT the benefit accruing from 'Golden Revolution'?
Increase in the income of the farmers.
Increase in production of milk and related products.
Increase in production and exports of fruits and vegetables.
Employment for women in rural areas.
Chapter: [0.02] Indian Economy 1950-1990
From the set of the events given in Column-I and the corresponding year in Column-II, choose the incorrect pair:
| Column-I | Column-II | ||
| A. | Introduction of railways in India | (i) | 1850 |
| B. | Incorporation of TISCO | (ii) | 1807 |
| C. | First official census of India | (iii) | 1881 |
| D. | Opening of suez canal | (iv) | 1869 |
A - (i)
B - (ii)
C - (iii)
D - (iv)
Chapter: [0.01] Indian Economy on the Eve of Independence
Advertisements
China initiated ______ in 1958, that aimed at industrializing the country on a massive scale.
The Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution
Setting up of Special Economic Zones
Introduction of Economic Reforms
The Great Leap Forward Campaign
Chapter: [0.1] Comparative Development Experiences of India and Its Neighbours
______ acts as a measure of 'the extent of democratic participation in social and political decision-making.'
Human Development Index
Liberty Indicator
Economic Growth
Poverty Index
Chapter: [0.1] Comparative Development Experiences of India and Its Neighbours
In an economy, when the rate of resource extraction is lower than the rate of regeneration of the resource, the environment may operate ______.
within its carrying capacity.
beyond its absorptive capacity.
beyond its carrying capacity.
beyond its aesthetic capacity.
Chapter: [0.09] Environment and Sustainable Development
Statement 1: Amongst India, China and Pakistan, China is the largest nation and has the higest population density.
Statement 2: One-child policy introduced in the late 1970s in china led to a considerable decline in the population growth rate.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative from the following:
Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
Statement 1 is false and Statement 2 is true.
Both Statements 1 and 2 are true.
Both Statements 1 and 2 are false.
Chapter: [0.1] Comparative Development Experiences of India and Its Neighbours
On the basis of the data given below, identify the incorrect statement in terms of annual growth of GDP (%): (Choose the correct alternative)
| Annual Growth of Gross Domestic Product (%) 1980-2017 | ||
| Country | 1980-90 | 2015-2017 |
| India | 5.7 | 7.3 |
| China | 10.3 | 6.8 |
| Pakistan | 6.3 | 5.3 |
China was able to maintain near double-digit growth during the 1980s.
Pakistan was ahead of India during 1980-2017.
India experienced a rapid rise in Gross Domestic Product during 2015-17.
Both China and Pakistan experienced a decline in growth rate during 2015-17.
Chapter: [0.1] Comparative Development Experiences of India and Its Neighbours
"Serious concerns over the climate change is taking over the attention of the world."

In the light of the above statement and image, discuss any two strategies to tackle this global concern of Environmental degradation.
Chapter: [0.09] Environment and Sustainable Development
"Recently the Government of India has taken numerous steps towards increasing the farmer's income through agricultural diversification."
In light of the above statement, explain any two advantages of diversification in agriculture.
Chapter: [0.02] Indian Economy 1950-1990
"Active Government intervention is essential in education and health sectors in India."
Do you agree with the given statement? Give reasons in support of your answer.
Chapter: [0.05] Human Capital Formation in India
Discuss any two merits and demerits of the Green Revolution in the agricultural sector in the Indian economy.
Chapter: [0.02] Indian Economy 1950-1990
On the basis of the given data:
| Some Selected Indicators of Human Development, 2017-2019 | |||
| Item | India | China | Pakistan |
| Human Development Index (Value) | 0.645 | 0.761 | 0.557 |
| Rank (based on HDI) | 130 | 87 | 154 |
| Life Expectancy at Birth (years) | 69.7 | 76.9 | 67.3 |
| Mean years of Schooling (% aged 15 and above) |
6.5 | 8.1 | 5.2 |
| Gross National Income per capita (PPP US$) | 6681 | 16.057 | 5005 |
| Percentage of people living Below Poverty Line (National) | 21.9* | 1.7** | 24.3* |
| Infant Mortality Rate (per 1000 live births) |
29.9 | 7.4 | 57.2 |
| Maternal Mortality Rate (per 1 lakh births) |
133 | 29 | 140 |
| Population using at least basic Sanitation (%) | 60 | 75 | 60 |
| Population using at least basic drinking Water Source (%) | 93 | 96 | 91 |
| Percentage of Undernourished Children | 37.9 | 8.1 | 37.6 |
- Identify one income indicator and one health indicator, each.
- Compare India and China on the basis of any one of the indicator identified above in part (i)
Chapter: [0.1] Comparative Development Experiences of India and Its Neighbours
"Expenditure on On-the-job training is an important means of human capital formation in an economy."
Give valid reasons to justify the given statement.
Chapter: [0.05] Human Capital Formation in India
“Organic Farming is the need of the hour to promote sustainable development but, has its own limitations.”
Elaborate any two advantages and limitations each of organic farming in the light of the above statement.
Chapter: [0.06] Rural Development
Define Worker Population Ratio. Discuss its usefulness.
Chapter: [0.07] Employment: Growth, Informalisation and Other Issues
‘Mr. Rishi, after completing his education, has joined his family business but his marginal productivity is zero.'
Comment upon the employment status of Mr. Rishi. Give valid reasons in support of your answer.
Chapter: [0.07] Employment: Growth, Informalisation and Other Issues
‘Kavya works on her family farm and is neither paid in cash nor in the form of grains.’
Can she be categorized as a worker? Give valid reasons in support of your answer.
Chapter: [0.07] Employment: Growth, Informalisation and Other Issues
“In the late 1990's India experienced a widening gap between the growth of GDP and employment generation”. Discuss.
Chapter: [0.07] Employment: Growth, Informalisation and Other Issues
Read the following text carefully and answer the given questions on the basis of the same and common understanding.
|
The stabilisation and structural adjustment measures, initiated under the 1991 “Economic Reforms” mark a watershed moment in India's economic policies. For almost three decades since independence, India’s development strategy and economic policies were guided by the objectives of accelerating the growth of output and employment with social justice and equity. Ever since the 1970s, it was realised that many of the regulations on economic activities have outlived their usefulness and were in fact hampering economic growth and development. In response to this, the government initiated some milder liberalisation reforms for almost a decade since the early 1980s. However, the Indian economy soon had to face the Gulf crisis and consequently:
These led to the Indian economy on the verge of Economic crisis. In response to this emerging crisis, the Government initiated a set of stabilisation and. structural reforms like:
The key objective of stabilisation policy was to bring the growth of aggregate demand in line with long term growth path of the economy. In conjunction, the structural adjustment measures like;
Were taken to improve the supply side of the economy. This shifted the long-term growth path of the economy itself completely. |
- Briefly outline any two reasons for the initiation of Economic Reforms in 1991.
- Government introduced a set of stablisation and structural reforms to solve the economic crisis. State the key initiatives and objectives of these policies adopted by the Government of India.
Chapter: [0.03] Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation : an Appraisal
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Economics with solutions 2022 - 2023
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Economics-2023 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Economics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Economics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
