Commerce (English Medium)
Arts (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2022-2023
Date: March 2023
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS :
- This question paper contains two sections:
Section A – Macro Economics
Section B – Indian Economic Development - This paper contains 20 Multiple Choice Questions type questions of 1 mark each.
- This paper contains 4 Short Answer Questions type questions of 3 marks each to be answered in 60 to 80 words.
- This paper contains 6 Short Answer Questions type questions of 4 marks each to be answered in 80 to 100 words.
- This paper contains 4 Long Answer Questions type questions of 6 marks each to be answered in 100 to 150 words.
Read the following statements carefully:
Statement 1: The consumption curve is an upward sloping straight line curve due to the direct relationship between income and consumption and the assumption of constant Marginal Propensity to Consume.
Statement 2: Aggregate Demand curve and Consumption curve are parallel to each other.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative from the following:
Statement 1 is true and statement 2 is false
Statement 1 is false and statement 2 is true
Both statements 1 and 2 are true
Both statements 1 and 2 are false
Chapter: [0.04] Determination of Income and Employment
‘Owing to the Russia-Ukraine crisis, the world is experiencing rising crude prices due to supply-side issues.’
Identify the most likely impact on the Balance of Payment situation of the Indian economy from the following:
Production of cars in India will rise.
Production and sale of cycles in India will rise.
Inflow of US Dollars in India will rise.
Outflow of US Dollars from India will rise.
Chapter: [0.06] Open Economy Macroeconomics
_________ is an institution that accept deposits for lending purposes.
Commercial Banks
Life Insurance Corporation
Reserve Bank of India
Government of India
Chapter: [0.03] Money and Banking
Read the following statements carefully:
Statement 1: Export of financial services by India will be recorded on credit side of current account.
Statement 2: Foreign Direct Investments in India will be recorded on credit side of capital account.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative:
Statement 1 is true and statement 2 is false
Statement 1 is false and statement 2 is true
Both statements 1 and 2 are true
Both statements 1 and 2 are false
Chapter: [0.06] Open Economy Macroeconomics
Read the following statements carefully:
Statement 1 - Net investment is a stock concept.
Statement 2 - Capital is a flow concept.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative from the following:
Statement 1 is true and statement 2 is false
Statement 1 is false and statement 2 is true
Both statements 1 and 2 are true
Both statements 1 and 2 are false
Chapter: [0.02] National Income and Related Aggregates
Read the following figure carefully and choose the correct pair from the alternatives given below:

Output, Production
Value added, Production
Output, Disposition
Wealth, Development
Chapter: [0.02] National Income and Related Aggregates
If in an economy, the value of investment multiplier is 4 and Autonomous Consumption is ₹ 30 Crore, the relevant consumption function would be :
C = 30 + 0.75 Y
C = (-) 30 + 0.25 Y
C = 30 - 0.75 Y
C = 30 - 0.25 Y
Chapter: [0.04] Determination of Income and Employment
If increase in National Income is equal to increase in consumption, identity the value of Marginal Propensity to Save:
Equal to unity
Greater than one
Less than one
Equal to zero
Chapter: [0.04] Determination of Income and Employment
Money supply in India may increase if, ______
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI) injects more money in circulation.
- The commercial banks expand their credit operation.
- Tax rates are reduced by the Central Government.
- Reserve Bank of India increases the Bank Rate.
1, 2 and 3 are correct.
2, 3 and 4 are correct.
1, 3 and 4 are correct.
1, 2 and 4 are correct.
Chapter: [0.03] Money and Banking
Suppose, following data is presented, for an imaginary economy:
| Year | Visible Exports | Visible Imports |
| 2010 | 280 | 240 |
| 2020 | 580 | 460 |
Identify, which of the statement about the period 2010 to 2020 is correct?
Improvement in balance of trade
Increase in trade deficit
Improvement in balance in invisibles items
Deterioration of balance of trade
Chapter: [0.06] Open Economy Macroeconomics
The following information is given for an imaginary country:
| Current Account | Amount (in ₹’000 Crore) |
| Visible Exports | 100 |
| Visible Imports | 150 |
| Invisible Exports | 70 |
| Invisible Imports | 30 |
| Net current transfer balance | 15 |
Balance on current account will be ____________ of ₹ ______ thousand Crore.
deficit, 10
surplus, 5
deficit, 5
surplus, 10
Chapter: [0.06] Open Economy Macroeconomics
Assertion (A): Ex-post Investments represent planned Investments; whereas ex-ante Investments represent actual level of investments.
Reason (R): At equilibrium level, Ex-ante Savings and Ex-ante Investments are always equal.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter: [0.04] Determination of Income and Employment
Assertion (A): Saving curve makes a negative intercept on the vertical axis at zero level of income.
Reason (R): Saving function refers to the functional relationship between saving and income.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter: [0.04] Determination of Income and Employment
Suppose in a hypothetical economy there are only two Firms A and B, Firm A sold goods for ₹ 2,000 to Firm B and purchased goods for ₹ 1,000. Firm B exported goods for ₹ 2,500 and had domestic sales of ₹ 1,500. Calculate Net Domestic Product at market price, if consumption of fixed capital is ₹ 200.
Chapter: [0.02] National Income and Related Aggregates
Explain, how exchange rate is determined under a free market exchange rate system.
Chapter: [0.06] Open Economy Macroeconomics
Distinguish between an autonomous transaction and accommodating transactions of the balance of payments account.
Chapter: [0.06] Open Economy Macroeconomics
If an economy plans to increase its income by ₹ 2,000 crore and the Marginal Propensity to Consume is 75%. Estimate the increase in investment required to achieve the targeted increase in income.
Chapter: [0.04] Determination of Income and Employment
As per the following news published in The Economic Times on 26th December, 2021:
‘Reserve Bank of India has sold government securities worth ₹ 8,710 crore in the secondary market, over the last four weeks, to drain out excessive liquidity’.
Identify the likely cause and the consequences behind, this type of action plan of the Reserve Bank.
Chapter: [0.03] Money and Banking
Read the following text carefully, discuss briefly the relevant function of the Central Bank, indicated :
Recently, Reserve Bank of India (RBI) conducted a statutory inspection for supervisory evaluation against a Commercial Bank. The commercial bank was imposed with stringent penalties, owing to deficiencies in regulatory compliances.
As per the Central Bank, the inspection revealed non-compliances vis-a-vis different directions issued by RBI, on the following fronts:
- ATM Card frauds
- Ensuring integrity and quality of data
- Loans to small borrowers
Chapter: [0.03] Money and Banking
Advertisements
‘Reserve Ratio and Credit Creation are inversely related.’ Do you agree with the given statement? Justify your answer with a suitable numerical example.
Chapter: [0.03] Money and Banking
Define Gross Domestic Product (GDP) deflator and discuss its importance.
Chapter: [0.02] National Income and Related Aggregates
State and discuss any two precautions to be considered while estimating national income by Expenditure Method.
Chapter: [0.02] National Income and Related Aggregates
Compare the trends depicted in the figures given below:
| Figure 1: Trends in Fiscal deficit and Primary deficit |
Figure 2: Fiscal deficit as a percent of Budget estimate |
 |
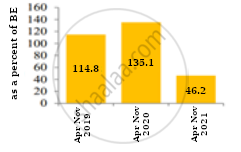 |
Chapter: [0.05] Government Budget and the Economy
Explain the ‘allocation of resources’ objective of Government budget.
Chapter: [0.05] Government Budget and the Economy
Distinguish between revenue receipts and capital receipts in a government budget. Give example in each case.
Chapter: [0.05] Government Budget and the Economy
Distinguish between direct taxes and indirect taxes. Give an example of each
Chapter: [0.05] Government Budget and the Economy
Identify, which of the following indicates the adverse impact of British rule in India.
Introduction of communication networks in India
Change in composition of India’s foreign trade
Introduction of modern administrative system in India
Introduction of railways in India
Chapter: [0.01] Indian Economy on the Eve of Independence
_________ committee was set up for the development and promotion of small scale industries in India.
Karve
Tapas Majumdar
Mahalanobis
TRYSEM
Chapter: [0.02] Indian Economy 1950-1990
First Industrial Policy Resolution of Independent India was announced in the year ______.
1947
1948
1951
1956
Chapter: [0.02] Indian Economy 1950-1990
________ and _____ are the reasons for the slowdown of the Pakistan economy since independence.
- political instability
- over-dependence on remittances from abroad
- stable performance of agriculture sector
- growth of service sector
I and II
II and III
III and IV
I and IV
Chapter: [0.1] Comparative Development Experiences of India and Its Neighbours
‘GLF’ with respect to the People’s Republic of China referred to as ______
Giant Leap Forward
Great Lead Forum
Great Leap Forward
Giant Lead Forum
Chapter: [0.1] Comparative Development Experiences of India and Its Neighbours
Identify which of the following is a source of non-institutional credit in the rural areas of India.
NABARD
Regional Rural Banks
Money Lenders
Commercial Banks
Chapter: [0.06] Rural Development
From the set of the events given in column I and corresponding facts given in Column II, choose the correct pair of statements:
| COLUMN I | COLUMN II | ||
| i | Dual Pricing | A | Economic Reforms of 1991 |
| ii | Setting up of Special Economic Zones in China | B | To attract foreign Direct Investment |
| iii | Commune System | C | Backyard based Industrial production units |
| iv | Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution | D | Collective Farming |
i – A
ii – B
iii – C
iv – D
Chapter: [0.1] Comparative Development Experiences of India and Its Neighbours
Read the following statements carefully.
Statement 1: On-the-job trainings help to bridge a gap between theoretical concepts and practical experiences.
Statement 2: On-the-job trainings update the employees, with the latest changes in their work field.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative:
Statement 1 is true and statement 2 is false
Statement 1 is false and statement 2 is true
Both statements 1 and 2 are true
Both statements 1 and 2 are false
Chapter: [0.05] Human Capital Formation in India
Read the following statements carefully.
Statement 1: Both India and Pakistan initiated their economic reforms without any external pressures.
Statement 2: Pakistan has successfully implemented the SEZ policy and reaped its benefits using the Export Promotion policy.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative:
Statement 1 is true and statement 2 is false.
Statement 1 is false and statement 2 is true.
Both statements 1 and 2 are true.
Both statements 1 and 2 are false.
Chapter: [0.1] Comparative Development Experiences of India and Its Neighbours
______ is not a cause for environmental degradation.
Waste management
Deforestation
Global warming
Guarding green cover
Chapter: [0.09] Environment and Sustainable Development
Advertisements
______ is not the strategy for Sustainable Development.
Use of bio-gas
Use of solar power
Use of thermal power
Use of hydel power
Chapter: [0.09] Environment and Sustainable Development
Assertion (A): Unemployment and poverty are inseparable twins.
Reason(R): Unemployment is the root cause of all socio-economic evils
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter: [0.04] Determination of Income and Employment [0.07] Employment: Growth, Informalisation and Other Issues
Assertion (A): In the late 1970s, China’s population growth rate had sharply declined.
Reason(R): China has witnessed an increase in the proportion of elderly people owing to stringent family planning programmes.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter: [0.1] Comparative Development Experiences of India and Its Neighbours
Interpret the given picture on account of current environmental challenges.

Chapter: [0.09] Environment and Sustainable Development
Defend or refute the following statement with a valid explanation:
‘Disguised unemployment is a common form of unemployment in rural India’
Defend
Refute
Chapter: [0.04] Determination of Income and Employment [0.07] Employment: Growth, Informalisation and Other Issues
Critically evaluate the role of the rural banking system in the process of rural development in India.
Chapter: [0.06] Rural Development
Compare and analyse the following information related to Imports and Exports of the three neighbouring nations:
| Country | Exports from India (in ₹ Crore) |
Imports to India (in ₹ Crore) | ||||
| 2004- 05 | 2018-19 | Annual rate of growth (%) | 2004-05 | 2018-19 | Annual rate of growth (%) | |
| Pakistan | 2,341 | 14,426 | 3.7 | 427 | 3,476 | 5.1 |
| China | 25,232 | 1,17,289 | 2.6 | 31,892 | 4,92,079 | 10.3 |
Chapter: [0.1] Comparative Development Experiences of India and Its Neighbours
Name any one Maharatana company.
Chapter: [0.03] Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation : an Appraisal
‘Land ceiling promotes equity.’ Support the given statement with valid explanation.
Chapter: [0.02] Indian Economy 1950-1990
Discuss briefly, how institutional reforms (land reforms) have played a significant role in transforming Indian agriculture.
Chapter: [0.02] Indian Economy 1950-1990
State whether the following statement is true/false, with valid argument:
Human Capital and Human Development are one and the same thing.
True
False
Chapter: [0.05] Human Capital Formation in India
State whether the following statement is true/false, with valid argument:
India has a poor stock of technical manpower.
True
False
Chapter: [0.04] Poverty
Define agricultural marketing.
Chapter: [0.06] Rural Development
Discuss briefly the importance of micro-credit programmes in rural development.
Chapter: [0.06] Rural Development
Enlist some problems faced by farmers during the initial years of organic farming.
Chapter: [0.06] Rural Development
“India has failed to implement the recommendations of Education Commission of 1964-66.” Give valid arguments in support of the given statement.
Chapter: [0.05] Human Capital Formation in India
‘Casual wage work is the major source of employment in rural India’. Defend or refute the given statement with a valid reason.
Defend
Refute
Chapter: [0.07] Employment: Growth, Informalisation and Other Issues
Read the following text carefully and answer the given questions on the basis of the same and common understanding:
|
The Green Revolution in India began in the mid-1960s marking a transition from traditional agriculture in India to high-yielding varieties of seeds and the associated modern agricultural techniques. The need for introduction of Green Revolution in India arose due to a shortage of food-grains in the post-independent period. he government in the post-independent India wanted to ensure self-dependence in terms of food-grain production. Such efforts coincided with the development of high-yielding varieties of seeds of wheat developed by Dr. Norman Borlung and his associates in Mexico. These seeds also necessitated changes in farming techniques such as the addition of fertilizers, pesticides and better irrigation facilities. High yielding varieties of seeds were first introduced in India in the states of Punjab, Haryana and parts of western Uttar Pradesh. In the early period of the green revolution in India, the focus was to acclimatise the new system with the more resource-intensive agricultural methods. The argument for introducing the new crop varieties was to increase agricultural production in terms of higher crop yields. The seeds introduced during the early period of the green revolution in Punjab were not highyielding by themselves. These high yields were possible due to the seeds being highly responsive to certain inputs such as irrigation water and fertilizers. The green revolution in India, thus, necessitated a resource-intensive process whereby, those who could make significant capital investments could benefit, whereas, those others became more marginalized in regions affected by practices of the green revolution in India. On one hand, the results derived from the green revolution helped farmers to increase their yield and income and on the other hand, it helped the government to procure and preserve more food grains through agencies like Food Corporation of India. These food grain reserves were helpful in creation of buffer stocks in India, which helped in the situations of adversities. |
- Why was Green revolution implemented and how did it benefit the farmers?
- Justify the following statement with valid explanation:
‘Green revolution enabled the government to procure sufficient food grains to build its stocks that could be used during time of shortage’.
Chapter: [0.02] Indian Economy 1950-1990
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Economics with solutions 2022 - 2023
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Economics-2023 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Economics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Economics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
