Commerce (English Medium)
Science (English Medium)
Arts (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2022-2023
Date & Time: 2nd March 2023, 10:30 am
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS -
- Question paper is divided into 4 sections A, B, C, & D and contains 30 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- In Section A - questions 1 to 17 are Multiple Choice Question type questions 1 mark each. Question No. 15 to 17 are Source-based Questions.
- In Section B - questions number 18 to 23 are Short Answer type questions (80-100 words) 3 marks each. Questions 18 & 19 are Source-based questions.
- In Section C - question number 24 to 28 are Long Answer type questions (120-150 words) 5 marks each.
- In Section D - question 29 and 30 are Map based questions having 5 subparts 5 marks each.
Who, among the following economists created the Human Development Index in the year 1990?
Prof. Amartya Sen
Dr. Manmohan Singh
Dr. Mahbub-ul-Haq
Ellen C. Semple
Chapter: [0.04] Human Development
Which one of the following approaches was initially proposed by the International Labour Organisation (ILO)?
Income Approach
Welfare Approach
Basic Needs Approach
Capability Approach
Chapter: [0.04] Human Development
Which of the following is NOT a key area in human development?
Access to resources
Long and healthy life
Education
Economic disadvantage
Chapter: [0.04] Human Development
In a developed economy, the majority of workers get employment in which of the following sectors of economy?
Primary sector
Secondary sector
Tertiary sector
Quaternary sector
Chapter: [0.07] Tertiary and Quaternary Activities
Which one of the following activities is related to quaternary activities?
Production of information
Fishing
Tourism
Trading
Chapter: [0.07] Tertiary and Quaternary Activities
Which one of the following is NOT a characteristic of retail trading?
It is concerned with sale of goods directly to the consumers.
Most of the retail trading takes place in fixed establishments.
Most of the retail stores procure their Supplies from -intermediate stores.
Retail trading constitutes bulk business through numerous intermediary merchants and-supply houses.
Chapter: [0.07] Tertiary and Quaternary Activities
Modern manufacturing is NOT characterised by which one of the following?
A complex machine technology
Vast capital
Small organisations
Executive bureaucracy
Chapter: [0.06] Secondary Activities
Identify the feature of mixed farming from the following:
It is most advanced and efficient type of reading milch animals.
Equal emphasis is laid on crop cultivation and animal husbandry.
It was introduced by the Europeans in colonies.
The regions where farmers specialised in vegetables only.
Chapter: [0.05] Primary Activities
Which of the following is an example of ancient town?
Hyderabad
Chennai
Prayag
Lucknow
Chapter: [0.04] Human Settlements
Which one of the following is NOT true about Bharmaur tribal region?
This region comprises of Bharmaur and Holi tehsil of Chamba district.
It is not a notified tribal area.
It is mainly inhabited by Gaddi tribal community.
The tribals practise transhumance.
Chapter: [0.09] Planning and Sustainable Development in Indian Context
Which of the following statement is NOT true regarding Indira Gandhi Canal?
It was previously known as Rajasthan canal.
It originates at Harika barrage in Punjab.
The canal runs almost parallel to Pakistan border.
Rajasthan is least benefitted by this canal.
Chapter: [0.09] Planning and Sustainable Development in Indian Context
Which of the following commission replaced 'Planning Commission'?
Election Commission
NITI Aayog
Law Commission
Education Commission
Chapter: [0.09] Planning and Sustainable Development in Indian Context
Advertisements
Choose the correct pair from the following:
Industrial town - Vishakhapatnam
Transport town - Satna
Commercial town - Bhilai
Administrative town - Bhopal
Chapter: [0.04] Human Settlements
Which one of the following is NOT a significant factor in creating noise pollution?
Mechanised construction
Automobiles
Fodder cutting machine
Variety of industries
Chapter: [0.12] Geographical Perspective on Selected Issues and Problems
|
A Case Study Jhabua district is located in the westernmost agro-climatic zone in Madhya Pradesh. It is, in fact, one of the five most backward districts of the country. It is characterised by high concentration of tribal population (mostly Bhils). The people suffer due to poverty which has been accentuated by the high rate of resource degradation, both forest and land. The watershed management programmes funded by both the ministries of “Rural Development” and “Agriculture”, Government of India, have been successfully implemented in Jhabua district which has gone a long way in preventing land degradation and improving soil quality. Watershed Management Programmes acknowledge the linkage between land, water and vegetation and attempts to improve livelihoods of people through natural resource management and community participation. In the past five years, the programmes funded by the Ministry of Rural Development alone (implemented by Rajiv Gandhi Mission for Watershed Management) has treated 20 percent of the total area under Jhabua district. The Petlawad Development block of Jhabua is located in the northermost part of the district and represents an interesting and successful case of Government-NGO partnership and community participation in managing watershed programmes. The Bhils in Petlawad Development block, for example, (Sat Rundi hamlet of Karravat village) through their own efforts, have revitalized large parts of common property resources. Each household planted and maintained one tree on the common property. They also have planted fodder grass on the pasture land and adopted social-fencing of these land for at least two years. Even after that, they say, there would be no open grazing on these lands, but stall feeding of cattle, and they are thus confident that the pastures they have developed would sustain their cattle in future. An interesting aspect this experience is that before the community embarked upon the process of management of the pasture, there was encroachment on this land by a villager from an adjoining village. The villagers called the tehsildar to ascertain the rights of the common land. The ensuing conflict was tackled by the villagers by offering to make the defaulter encroaching on the CPR a member of their user group and sharing the benefits of greening the common lands/pastures. |
Why did the people of Jhabua tribal community suffer from poverty? Choose the option which is NOT correct.
High rate of forest degradation
Land degradation
Illiteracy
Implementation of watershed management
Chapter: [0.12] Geographical Perspective on Selected Issues and Problems
|
A Case Study Jhabua district is located in the westernmost agro-climatic zone in Madhya Pradesh. It is, in fact, one of the five most backward districts of the country. It is characterised by high concentration of tribal population (mostly Bhils). The people suffer due to poverty which has been accentuated by the high rate of resource degradation, both forest and land. The watershed management programmes funded by both the ministries of “Rural Development” and “Agriculture”, Government of India, have been successfully implemented in Jhabua district which has gone a long way in preventing land degradation and improving soil quality. Watershed Management Programmes acknowledge the linkage between land, water and vegetation and attempts to improve livelihoods of people through natural resource management and community participation. In the past five years, the programmes funded by the Ministry of Rural Development alone (implemented by Rajiv Gandhi Mission for Watershed Management) has treated 20 percent of the total area under Jhabua district. The Petlawad Development block of Jhabua is located in the northermost part of the district and represents an interesting and successful case of Government-NGO partnership and community participation in managing watershed programmes. The Bhils in Petlawad Development block, for example, (Sat Rundi hamlet of Karravat village) through their own efforts, have revitalized large parts of common property resources. Each household planted and maintained one tree on the common property. They also have planted fodder grass on the pasture land and adopted social-fencing of these land for at least two years. Even after that, they say, there would be no open grazing on these lands, but stall feeding of cattle, and they are thus confident that the pastures they have developed would sustain their cattle in future. An interesting aspect this experience is that before the community embarked upon the process of management of the pasture, there was encroachment on this land by a villager from an adjoining village. The villagers called the tehsildar to ascertain the rights of the common land. The ensuing conflict was tackled by the villagers by offering to make the defaulter encroaching on the CPR a member of their user group and sharing the benefits of greening the common lands/pastures. |
How did people manage to develop pasture lands? Choose the correct option.
Use of barbed wire to protect pastures
Pasture lands were not under any encroachment
Pastures were common property resources, hence they developed it
Govt. officials did not interfere in any work of the villagers
Chapter: [0.12] Geographical Perspective on Selected Issues and Problems
|
A Case Study Jhabua district is located in the westernmost agro-climatic zone in Madhya Pradesh. It is, in fact, one of the five most backward districts of the country. It is characterised by high concentration of tribal population (mostly Bhils). The people suffer due to poverty which has been accentuated by the high rate of resource degradation, both forest and land. The watershed management programmes funded by both the ministries of “Rural Development” and “Agriculture”, Government of India, have been successfully implemented in Jhabua district which has gone a long way in preventing land degradation and improving soil quality. Watershed Management Programmes acknowledge the linkage between land, water and vegetation and attempts to improve livelihoods of people through natural resource management and community participation. In the past five years, the programmes funded by the Ministry of Rural Development alone (implemented by Rajiv Gandhi Mission for Watershed Management) has treated 20 percent of the total area under Jhabua district. The Petlawad Development block of Jhabua is located in the northermost part of the district and represents an interesting and successful case of Government-NGO partnership and community participation in managing watershed programmes. The Bhils in Petlawad Development block, for example, (Sat Rundi hamlet of Karravat village) through their own efforts, have revitalized large parts of common property resources. Each household planted and maintained one tree on the common property. They also have planted fodder grass on the pasture land and adopted social-fencing of these land for at least two years. Even after that, they say, there would be no open grazing on these lands, but stall feeding of cattle, and they are thus confident that the pastures they have developed would sustain their cattle in future. An interesting aspect this experience is that before the community embarked upon the process of management of the pasture, there was encroachment on this land by a villager from an adjoining village. The villagers called the tehsildar to ascertain the rights of the common land. The ensuing conflict was tackled by the villagers by offering to make the defaulter encroaching on the CPR a member of their user group and sharing the benefits of greening the common lands/pastures. |
How did the Bhils, through their own efforts revitalise the common property resources? Choose the correct option.
Common land was brought tinder cultivation
They controlled open grazing on the common property resources
No tree plantation was taken up
They developed water resources
Chapter: [0.12] Geographical Perspective on Selected Issues and Problems
Read the given source and answer the questions that follow:
|
We use many items in our daily life. From toothpaste to our bed tea, milk, clothes, soaps, food items, etc., are required every day. All these can be purchased from the market. Have you ever thought as to how these items are brought from the site of production? All the production is meant for consumption. From the fields and factory, the produce is brought to the place from where consumers purchase it. It is the transportation of these items from the site of their production to the market which make them available to the consumer. We not only use material things, like fruits, vegetables, books, clothes, etc., but also use ideas, views and messages in our daily life. Do you know we exchange our views, ideas and messages from one place to another or one individual to another while communicating with the help of various means? The use of transport and communication depends upon our need to move things from place of their availability to the place of their use. Human beings use various methods to move goods, commodities, ideas from one place to another. |
- Explain the utility of transportation.
- Define the term 'Communication'.
- Differentiate between Transport and Communication.
Chapter: [0.08] Transport and Communication [0.1] Transport and Communication
Study the given figure carefully and answer the questions that follow:

- Name the highest populous country.
- How many total countries of Asia continent are shown in the figure?
- How do landforms affect the density of population in Asia.
Chapter: [0.02] The World Population - Distribution, Density and Growth
"The physical and human phenomena are described in metaphors using symbols from human anatomy." Support the statement with example.
Chapter: [0.01] Human Geography - Nature and Scope
"Technological innovations through research and development strategy are an important aspect of modern manufacturing''. Analyse the statement.
Chapter: [0.06] Secondary Activities
"Speedy and efficient system of transport is essential for the development of industries." Analyse the statement.
Chapter: [0.06] Secondary Activities
Explain how the 'size of population' and the stage of 'economic development' are the bases of international trade.
Chapter: [0.09] International Trade
Advertisements
"There is high demand of water for irrigation in agricultural sector in India." Justify the statement.
Chapter: [0.06] Water Resources
"Rain-water harvesting has been practised through various methods by different communities in the country." Justify the statement.
Chapter: [0.06] Water Resources
Analyse the effects of geographical factors on the distribution of world population.
Chapter: [0.01] Population : Distribution, Density, Growth and Composition
Analyse the economic factors affecting the distribution of population in the world.
Chapter: [0.01] Population : Distribution, Density, Growth and Composition
Analyse the social factors affecting the distribution of population in the world.
Chapter: [0.01] Population : Distribution, Density, Growth and Composition
Mention the major problems faced by global road transport in mountainous and hot desert areas.
Chapter: [0.08] Transport and Communication
Mention the major benefits of rail transport in the world.
Chapter: [0.08] Transport and Communication
"The uneven spatial distribution of population suggests a close relationship between population and socio-economic and physical factors." Analyse the statement.
Chapter: [0.01] Population : Distribution, Density, Growth and Composition
Examine the role of air transport in the promotion of international trade.
Chapter: [0.11] International Trade
Analyse any five problems faced by Indian farmers in agriculture.
Chapter: [0.05] Land Resources and Agriculture
On the given political outline map of the world seven geographical features have been marked as A, B, C, D, E, F and G. Identify any five and names them on the lines marked near them:
- An International Airport in Asia.
- A canal linking Red sea with Mediterranean sea.
- A major seaport in North America.
- A terminal station on the Trans-Australian Railway.
- A major area of nomadic herding in Africa.
- A major area of extensive commercial grain farming.
- International airport of Europe.
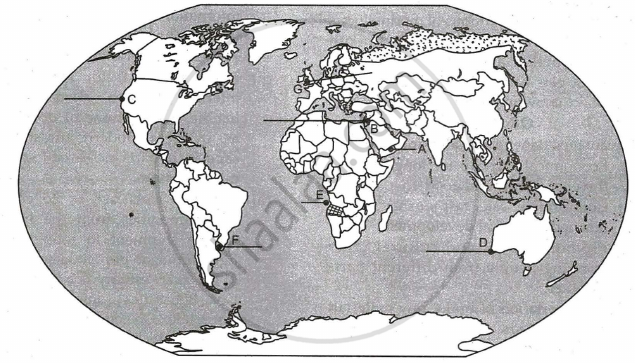
Chapter: [0.08] Transport and Communication
On the given political outline Map of India, locate and label any five of the following:
- A State with highest level of population density.
- State with the highest level of urbanisation.
- A state leading in the production of jute.
- Koraput-bauxite mines.
- Jharia coal mines.
- Mangaluru seaport.
- An international - airport in Punjab.
Chapter: [0.01] Population : Distribution, Density, Growth and Composition [0.02] The World Population - Distribution, Density and Growth
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Geography with solutions 2022 - 2023
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Geography-2023 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Geography, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Geography will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
