Advertisements
Advertisements
Verify if the following proposition is valid using the truth table:
(X ∧ Y) =>Z = (Y => Z) ∧ (X => Y).
Concept: Truth Tables
When a sequence of OR, NOT, NOR are connected in series, the logic gate obtained is ______.
Concept: Applications of Boolean Algebra and Logic Gates to Half Adders, Full Adders, Encoders, Decoders, Multiplexers, NAND, NOR as Universal Gates
Idempotence Law states that ______.
Concept: Applications of Boolean Algebra and Logic Gates to Half Adders, Full Adders, Encoders, Decoders, Multiplexers, NAND, NOR as Universal Gates
Draw the logic gate diagram for the reduced expression. Assume that the variables and their complements are available as inputs.
Concept: Applications of Boolean Algebra and Logic Gates to Half Adders, Full Adders, Encoders, Decoders, Multiplexers, NAND, NOR as Universal Gates
Draw the logic gate diagram for 2-input OR gate using NAND gates only. Show the expression at each Step.
Concept: Elementary Logic Gates (NOT, AND, OR, NAND, NOR, XOR, XNOR) and Their Use in Circuits
Draw the logic circuit for 3:8 decoder (Octal decoder). Which multiplexer can be derived from the Octal decoder?
Concept: Applications of Boolean Algebra and Logic Gates to Half Adders, Full Adders, Encoders, Decoders, Multiplexers, NAND, NOR as Universal Gates
A full adder needs five gates and those are 3 AND gates, 1 OR gate and 1 XOR gate. When a full adder is constructed using 2 half adders, it also requires 5 gates. State the names along with the quantity those gates.
Concept: Elementary Logic Gates (NOT, AND, OR, NAND, NOR, XOR, XNOR) and Their Use in Circuits
Draw the logic gate diagram for the reduced expression. Assume that the variables and their complements are available as inputs.
Concept: Elementary Logic Gates (NOT, AND, OR, NAND, NOR, XOR, XNOR) and Their Use in Circuits
Draw the logic circuit to decode the following binary number (0001, 0101, 0111, 1000, 1010, 1100, 1110,1111) to its hexadecimal equivalents. Also, state the Hexadecimal equivalents of the given binary numbers.
Concept: Applications of Boolean Algebra and Logic Gates to Half Adders, Full Adders, Encoders, Decoders, Multiplexers, NAND, NOR as Universal Gates
Answer the following questions related to the below image:
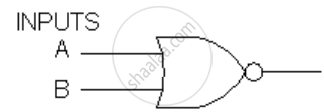
- What is the output of the above gate if input A=0, B=1?
- What are the values of the inputs if output =1?
Concept: Elementary Logic Gates (NOT, AND, OR, NAND, NOR, XOR, XNOR) and Their Use in Circuits
Write the canonical form of the cardinal terms, m3 and M5 for F (A, B, C, D).
Concept: Programming in Java (Review of Class Xi Sections B and C)
A class Ins Sort contains an array of integers which sorts the elements in a particular order.
Some of the members of the class are given below.
| Class name | InsSort |
| arr[ ] | stores the array elements |
| size | stores the number of elements in the array |
| Methods/Member functions: | |
| InsSort(int s) | constructor to initialise size= s |
| void getArray( ) | accepts the array elements |
| void insertionSornt( ) | sorts the elements of the array in descending order using the in descending order using the Insertion Sort technique |
| double find( ) | calculates and returns the average of all the odd numbers in the array |
| void display( ) | displays the elements of the array in a sorted order along with the average of all the odd numbers in the array by invoking the function find( ) with an appropriate message |
Specify the class InsSort giving details of the constructor(), void getArray( ), void insertionSort( ), double find() and void display(). Define a main( ) function to create an object and call all the functions accordingly to enable the task.
Concept: Programming in Java (Review of Class Xi Sections B and C)
Design a class Coding to perform some string related operations on a word containing alphabets only.
Example: Input: "Java"
Output: Original word: Java
J=74
a=97
v= 118
a=97
Lowest ASCII code: 74
Highest ASCII code: 118
Some of the members of the class are given below:
| Class name | Coding |
| Data members/instance variables: | |
| wrd | stores the word |
| len | stores the length of the word |
| Methods/Member functions: | |
| Coding() | constructor to initialise the data members with legal initial values |
| void accept( ) | to accept a word |
| void find() | to display all the characters of 'wrd' along with their ASCII codes. Also display the lowest ASCII code and the highest ASCII code, in 'wrd' |
| void show() | to display the original word and all the characters of 'wrd' along with their ASCII codes. Also display the lowest ASCII code and the highest ASCII code in 'wrd', by invoking the function find() |
Specify the class Coding giving details of the constructor( ), void accept( ), void find( ) and void show(). Define a main() function to create an object and call all the functions accordingly to enable the task.
Concept: Programming in Java (Review of Class Xi Sections B and C)
State any one difference between instance variable and class variable.
Concept: Object as an Instance of a Class
Consider the following statement written in class Circle where pi is its data member.
static final double pi = 3.142;
Which of the following statements are valid for pi?
- It contains a common value for all objects class Circle.
- Its value is non-changeable.
- At a time two access modifiers, static and final, cannot be applied to a single data member pi.
Concept: Object as an Instance of a Class
The following function is a part of some class which is used to find the smallest digit present in a number. There are some places in the code marked by ?1?, ?2?, ?3? which must be replaced by an expression/a statement so that the function works correctly.
int small_dig(int n)
{ int min=?1?;
while(n!=0)
{
int q=n/10;
int r=?2?*10;
min=r>min ? ?3? : r;
n=q;
}
return min;
}
- What is the expression or statement at ?1?
- What is the expression or statement at ?2?
- What is the expression or statement at ?3?
Concept: Looping (For, While-do, Do-while, Continue, Break)
int Toy(int n)
{ return (n<=0)? 1: n%10 + Toy(n/10); }With reference to the program code given above, what will the function Toy() return when the value of n = 56?
Concept: Structured Data Types - Arrays (Single and Multi-dimensional), Strings
Write the statement in Java to extract the word “MISS” from the word “SUBMISSION”.
Concept: Example Algorithms that Use Structured Data Types (E.G. Searching, Finding Maximum/Minimum, Sorting Techniques, Solving Systems of Linear Equations, Substring, Concatenation, Length, Access to Char in String, Etc.)
What is the output of the statement given below?
System.out.print("FAN" + ("AUTOMATIC".charAt(5) ) );Concept: Example Algorithms that Use Structured Data Types (E.G. Searching, Finding Maximum/Minimum, Sorting Techniques, Solving Systems of Linear Equations, Substring, Concatenation, Length, Access to Char in String, Etc.)
Design a class Check which checks whether a word is a palindrome or not.
(Palindrome words are those which spell the same from either ends).
Example: MADAM, LEVEL etc.
The details of the members of the class are given below:
| Class name | Check |
| Data members/instance variables: | |
| wrd | stores a word |
| len | to store the length of the word |
| Methods/Member functions: | |
| Check( ) | default constructor |
| void acceptword( ) | to accept the word |
| boolean palindrome( ) | checks and returns ‘true’ if the word is a palindrome otherwise returns ‘false’ |
| void display( ) | displays the word along with an appropriate message |
Specify the class Check giving details of the constructor, void acceptword( ), boolean palindrome( ) and void display( ). Define the main( ) function to create an object and call the functions accordingly to enable the task.
Concept: Basic Input/Output Using Scanner and Printer Classes from JDK
