Advertisements
Advertisements
Expand the following abbreviation:
PID
Concept: Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)
According to a survey conducted by the Government of India in the year 1950, the population of the country was 350 million. In the next survey conducted in the year 2010, the population had reached above 1000 million.
- List any two reasons for this rise in the population.
- Suggest any two steps which should be taken by the Government to control this rise.
- How does the population explosion affect the growth of a country?
- What is the difference between the natural and artificial contraceptive methods? Give one example of each method.
Concept: Population Explosion - Rising Population a Global Threat
Name any two Cu-ions releasing IUDs.
Concept: Infertility
Explain any two ways by which IUDs devices act as contraceptives.
Concept: Infertility
|
Sapna has been diagnosed with an infection of the reproductive tract caused by bacteria. She experiences burning sensation during urination, pain around her genitalia and observes pus containing discharge. Her doctor tells her that this infection has an incubation period of two to five days but can be cured. |
What is the biological name of the causative agent of the disease Sapna is suffering from?
Concept: Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)
Which is the most commonly prescribed non-steroidal oral contraceptive pill in India?
Concept: Reproductive Health
Which is the most commonly prescribed non-steroidal oral contraceptive pill in India?
Concept: Reproductive Health
Which one of the following choices reflects the correct number of chromosomes in the zygote and in the second polar body of Drosophila melanogaster?
| Zygote | Meiocytes | |
| I | 08 | 08 |
| II | 04 | 08 |
| III | 08 | 04 |
| IV | 04 | 04 |
Concept: Infertility
All STDs do not affect the genital organs. Justify the statement.
Concept: Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)
Define the following:
test cross.
Concept: Linkage and Crossing Over
The genotype of a person withTumer's syndrome will be:
(i) 44+XXY
(ii) 44+XYY
(iii) 44+XO
(iv) 44+XXYY
Concept: Genetic Disorders
Give any four reasons for Mendel's success.
Concept: Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity
Mention one significant difference between Epistasis and dominance
Concept: Extensions of Mendelian Genetics (Deviation from Mendelism)
A woman with blood group O married a man with blood group AB shows the possible blood groups of the progeny. List the alleles involved in this inheritance.
Concept: Extensions of Mendelian Genetics (Deviation from Mendelism)
If the mother is a carrier of colour blindness and the father is normal, the possible genotype and
the phenotype of the offspring of the next generation, with the help of a punnet square
Concept: Extensions of Mendelian Genetics (Deviation from Mendelism)
Answer the following question:
How many chromosomes are present in meiocytes of a fruit fly?
Concept: Sex Determination > Sex Determination in Birds
Choose the correct options of the following question:
Study the given monohybrid cross:
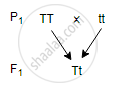
A test cross for this Fj will be:
Concept: Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
Choose the correct options of the following question:
In the given pedigree chart, the trait shown is:
Concept: Extensions of Mendelian Genetics (Deviation from Mendelism)
Define the Homologous chromosomes
Concept: Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
Give a scientific term for the following:
An alternative form of the single gene which influences the same character and produces different expressions in different individuals a species.
Concept: Extensions of Mendelian Genetics (Deviation from Mendelism)
