Advertisements
Advertisements
What are the reactions involved for ozone layer depletion in the stratosphere?
Concept: undefined > undefined
The reaction, \[\ce{CO(g) + 3H2(g) ↔ CH4(g) + H2O(g)}\] is at equilibrium at 1300 K in a 1L flask. It also contains 0.30 mol of CO, 0.10 mol of H2 and 0.02 mol of H2O and an unknown amount of CH4 in the flask. Determine the concentration of CH4 in the mixture. The equilibrium constant, Kc for the reaction at the given temperature is 3.90.
Concept: undefined > undefined
Advertisements
For the following bond cleavages, use curved arrows to show the electron flow and classify homolysis or heterolysis. Identify reactive intermediate produced as free radical, carbocation and carbanion.
\[\ce{CH3O - OCH3 -> CH3\overset\bullet{\text{O}} + \overset\bullet{\text{O}}CH3}\]
Concept: undefined > undefined
For the following bond cleavages, use curved-arrows to show the electron flow and classify as homolysis or heterolysis. Identify reactive intermediate produced as free radical, carbocation and carbanion.
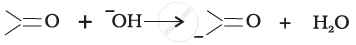
Concept: undefined > undefined
Draw the resonance structure for the following compound. Show the electron shift using curved-arrow notation.
\[\ce{CH3CH = CH\overset{+}{C}H2}\]
Concept: undefined > undefined
Why do elements in the same group have similar physical and chemical properties?
Concept: undefined > undefined
Suppose, the electron in a hydrogen atom makes transition from n = 3 to n = 2 in 10−8 s. The order of the torque acting on the electron in this period, using the relation between torque and angular momentum as discussed in the chapter on rotational mechanics is
Concept: undefined > undefined
