Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
![Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE chapter 4 - Simple Machines Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE chapter 4 - Simple Machines - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-physics-english-class-6-icse_6:a1d164c7b3a94be69d1611b80e82a122.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 4: Simple Machines
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 4 of CISCE Selina for Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE 4 Simple Machines Objective questions
State whether the following statement is True or False.
A boy does work while pushing a wall.
True
False
State whether the following statement is True or False.
A machine performs work by itself.
True
False
State whether the following statement is True or False.
In an ideal machine, work done on load is equal to the work done by effort.
True
False
State whether the following statement is True or False.
All levers are force multipliers.
True
False
State whether the following statement is True or False.
A pulley changes the direction of force.
True
False
State whether the following statement is True or False.
An inclined plane always has the mechanical advantage of more than 1.
True
False
Fill in the blank:
The useful work done by an actual machine is always ............ than the work done on the machine.
Fill in the blank:
In class II levers, the load is in between fulcrum and .........
Fill in the blank:
The mechanical advantage of class .............. lever is always less than 1.
Fill in the blank:
A pulley is used to change ........................
Fill in the blank:
Mechanical advantage of an inclined plane is always .................
Match the following:
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) Needle | (1) class II lever |
| (b) Doorknob | (2) inclined plane |
| (c) Ramp | (3) Class I lever |
| (d) Lemon crusher | (4) Wheel and axle |
| (e) Seesaw | (5) wedge |
Select the correct alternative:
For an ideal machine, the efficiency is
greater than unity
less than unity
equal to unity
depends on the value of load
Select the correct alternative:
Mechanical advantage of a machine is defined as:
Load X Effort
Load / Effort
Load + Effort
Effort / Load
The mechanical advantage of a lever is equal to ______.
`"Load arm"/"Effort arm"`
`"Effort arm"/"Load arm"`
Load arm + Effort arm
Load arm - Effort arm
Select the correct alternative:
A pulley is used because of it
has the mechanical advantage greater than one
has 100% efficiency
helps to apply the force in a convenient direction
requires more effort to raise a less load.
Select the correct alternative:
Wheel is used with axle because
sliding friction is less than the roffing friction
rolling friction is less than the sliding friction
they work as the inclined plane
They help us to change the direction of force.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE 4 Simple Machines Short/Long answer questions
When is work said to be done by a force?
What is energy?
What do you understand by a machine?
What is the principle on which a machine works?
State two functions of a machine.
Name six simple machines. Give an example of each machine.
Define the term ‘work input’ and ‘work output’ in relation to a machine.
Explain the term mechanical advantage.
Define the term efficiency of a machine.
What is an ideal machine?
Can a machine have an efficiency of 100%? Give a reason to support your answer.
A machine is 75% efficient’. What do you understand by this statement?
What is a lever?
Describe three orders of levers giving an example of each. Draw neat diagrams showing the positions of fulcrum, load, and effort in each kind of lever.
What do you mean by the mechanical advantage of a lever?
Which class of lever has the mechanical advantage always more than 1? Give an example.
Which class of lever has the mechanical advantage always less than 1? Give an example.
Give one example of a class I lever where the mechanical advantage is more than 1.
Give one example of a class I lever in a case where the mechanical advantage is equal to 1?
Give one example of a class I lever in a case where the mechanical advantage is less than 1?
Name the class to which the following lever belong:
A pair of scissors
Name the class to which the following lever belong:
a lemon squeezer
Name the class to which the following lever belong:
a nutcracker
Name the class to which the following lever belong:
a pair of sugar tongs
Name the class to which the following lever belong:
a beam balance
Name the class to which the following lever belong:
an oar rowing a boat.
Name the class to which the following lever belong:
a wheelbarrow
Name the class to which the following lever belong:
a see-saw
Name the class to which the following levers belong:
a pair of pliers
Name the class to which the following lever belong:
a crowbar
The diagram given below shows the three kinds of levers. Name the class of lever and give one example of the class.

The diagram given below shows the three kinds of levers. Name the class of lever and give one example of the class.

The diagram given below shows the three kinds of levers. Name the class of lever and give one example of the class.
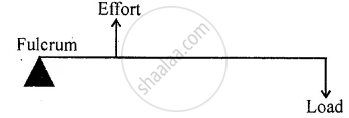
Draw diagram to illustrate the position of fulcrum, load, and effort, of the following:
a see-saw.
Draw diagram to illustrate the position of fulcrum, load, and effort, of the following:
a beam balance
Draw diagram to illustrate the position of fulcrum, load, and effort, of the following:
a nutcracker
Draw diagram to illustrate the position of fulcrum, load, and effort, of the following:
a pair of forceps
How can you increase the mechanical advantage of a lever?
How does the friction at the fulcrum affect the mechanical advantage of the lever?
State three differences between the three classes of levers.
What is a pulley?
What is the mechanical advantage of an ideal pulley?
The mechanical advantage of an actual pulley is less than one. Give a reason. What is the justification for using the pulley then?
Draw a neat labelled diagram showing a pulley being used to lift a load. How are load and effort related in an ideal situation?
What is an inclined plane?
What is a screw? Give two examples.
What are the wheel and axle? Give two examples.
How does a wheel help in moving the axle?
What is a wedge? Give two examples.
Name the machine to which the following belong:
Beam balance
Name the machine to which the following belong:
Lemon crusher
Name the machine to which the following belong:
Sugar tongs
Name the machine to which the following belong:
Ramp
Name the machine to which the following belong:
Doorknob
Name the machine to which the following belong:
Needle
What care would you take to increase the life span of a machine which you use?
Select the correct statement :
(a) A wheel barrow is a lever of class I.
(b) The efficiency of a machine is always 100%
(c) Friction in moving parts of a machine reduces its efficiency.
(d) No lever has the mechanical advantage greater than 1.
(e) It is easier to lift a load vertically up than to push it along an inclined plane.
(f) A screw is made by two inclined planes placed together.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE 4 Simple Machines Numericals
In a machine, an effort of 10 kgf is applied to lift a load of 100 kgf. What is its mechanical advantage?
The mechanical advantage of a machine is 5. How much load it can exert for the effort of 2 kgf?
The mechanical advantage of a machine is 2. It is used to raise a load of 15 kgf. What effort is needed?
A lever of length 100 cm has the effort of 15 kgf at a distance of 40 cm from the fulcrum at one end. What load can be applied at its other end?
In a lever, the fulcrum is at one end at a distance of 30 cm from the load and effort is at the other end at a distance of 90 cm from the load. Find :
(a) the length of load arm,
(b) the length of effort arm, and
(c) the mechanical advantage of the lever.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE 4 Simple Machines Additional questions
Answer the following.
What is a machine?
Answer the following.
What do you understand by a complex machine?
Answer the following.
Name the simplest of all types of machines.
Answer the following.
State the principle of levers.
Answer the following.
What is a Class I lever?
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE 4 Simple Machines Exercises 1
Tick the most appropriate answer.
The force applied on a machine to do work is called the
load
effort
efficiency
fulcrum
Tick the most appropriate answer.
If the effort lies between the fulcrum and the load, then the lever belongs to which class?
Class I
Class II
Class III
Class IV
Tick the most appropriate answer.
Which of the following is a Class II lever?
Pliers
A beam balance
A nut-cracker
A knife
Tick the most appropriate answer.
A pair of scissors is an example of a/an
wedge
lever
inclined plane
screw
Tick the most appropriate answer.
The mechanical advantage of an inclined plane is always
greater than 1
less than 1
equal to 1
zero
Tick the most appropriate answer.
The effort required to lift a load of 800 N by using a lever having a mechanical advantage of 1.6 is
1080 N
240 N
720 N
500 N
Tick the most appropriate answer.
A machine made up of two or more sloping surface is known as a
wedge
screw
pulley
lever
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE 4 Simple Machines Exercises 2
State if the following statement is true or false. Correct the statement if it is false.
There are four types of simple machines.
True
False
State if the following statement is true or false. Correct the statement if it is false.
The load and effort can act at a single point in a lever.
True
False
State if the following statement is true or false. Correct the statement if it is false.
A screw is a special case of an inclined plane.
True
False
State if the following statement is true or false. Correct the statement if it is false.
The effort required to insert a screw into wood is less than that needed to insert a nail into wood.
True
False
State if the following statement is true or false. Correct the statement if it is false.
A single movable pulley is a pulley that has its axis of rotation fixed.
True
False
State if the following statement is true or false. Correct the statement if it is false.
A rotation spindle tap is an example of a wheel-and-axle arrangement.
True
False
State if the following statement is true or false. Correct the statement if it is false.
A sewing needle is a wedge type simple machine.
True
False
State if the following statement is true or false. Correct the statement if it is false.
Work done by a machine is always more than the work done on a machine.
True
False
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE 4 Simple Machines Exercises 3
Answer the following in a word or two or in a sentence.
Given an example of a Class I lever.
Answer the following in a word or two or in a sentence.
Which type of machine is used to squeeze a lemon?
Answer the following in a word or two or in a sentence.
Write the relationship between mechanical advantage, load, and effort.
Answer the following in a word or two or in a sentence.
Name the type of machine made by putting two inclined planes together.
Answer the following in a word or two or in a sentence.
Give one example of a machine used to multiply speed.
Answer the following in a word or two or in a sentence.
Write the formula for calculating the efficiency of a machine.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE 4 Simple Machines Exercises 4
Answer the following in short.
Explain the various functions that a machine can perform.
Answer the following in short.
What is the basis of the classification of levers?
Answer the following in short.
What is the function of a screw? Give anyone the use of a screw.
Answer the following in short.
Using a suitable example, describe how a machine acts as a force multiplier.
Answer the following in short.
What do you understand by the term efficiency of a machine’?
Answer the following in short.
Mention any two methods by which we can take care of machines.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE 4 Simple Machines Exercises 5
Answer the following in detail.
Draw simplified diagrams by clearly showing the position of load, effort, and fulcrum for Class I, Class II, and Class III levers.
Answer the following in detail.
How does a pulley make work simpler?
Differentiate between a single fixed pulley and a single movable pulley.
Answer the following in detail.
What is a wedge? Explain the principle on which it works by giving suitable examples.
Answer the following in detail.
What is an inclined plane?
What is an inclined plane?
What is the use of inclined plane?
Give two examples where inclined plane is used.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE 4 Simple Machines Exercises 6
Give a reason for the following.
Machines are able to make our work convenient.
Give a reason for the following.
The efficiency of a machine is always less than 100%.
Give a reason for the following.
The front end of a boat is shaped like a wedge.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE 4 Simple Machines Exercises 7
Solve the following numerical problem.
The length of a lever is 2 m. Calculate its mechanical advantage if the fulcrum is situated at a distance of 40 cm from the effort.
Solve the following numerical problem.
The length of the load arm of a lever is 6 m long and the effort arm is 3 m long. What is the effort required to lift a load of 40 N?
Solve the following numerical problem.
Calculate the mechanical advantage of a crowbar of length 240 cm if its fulcrum is situated at a distance of 40 cm from the load.
Solve the following numerical problem.
What effort will be required to lift a load of 500 N by a single movable pulley? [Hint: Mechanical advantage of a single movable pulley is two].
Solutions for 4: Simple Machines
![Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE chapter 4 - Simple Machines Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE chapter 4 - Simple Machines - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-physics-english-class-6-icse_6:a1d164c7b3a94be69d1611b80e82a122.jpg)
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE chapter 4 - Simple Machines
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE CISCE 4 (Simple Machines) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE chapter 4 Simple Machines are Energy, Concept of Work, Machines, Principle of Machine, Efficiency of a Machine, Mechanical Advantage, Simple Machines, A Lever, Types of Levers, A Pulley, A Wheel and Axle, An Inclined Plane, A Wedge, Screw, Care of Machines, Machines (Numerical).
Using Selina Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE solutions Simple Machines exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 4, Simple Machines Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Concise Physics [English] Class 6 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
