Biogas is a renewable gaseous energy source produced from organic materials such as agricultural waste, manure, municipal waste, plant matter, sewage, green waste, wastewater, and food waste. It is generated through anaerobic digestion, a process in which anaerobic microorganisms or methanogens break down the organic material within an anaerobic digester, biodigester, or bioreactor.
- The primary components of biogas are methane (CH₄) and carbon dioxide (CO₂), along with trace amounts of hydrogen sulphide (H₂S), moisture, and siloxanes.
- The methane in biogas can be combusted or oxidised with oxygen, releasing energy that can be utilised as fuel. Biogas is commonly used for heating, such as in cooking, and can also power fuel cells. Additionally, it can be employed in gas engines to convert its energy into electricity and heat.
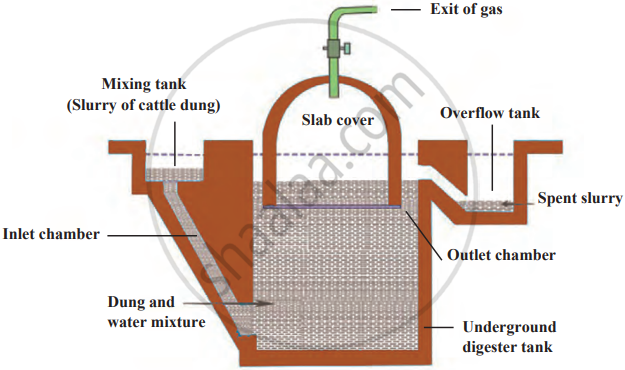
- Biogas is a very cheap fuel option that meets the demand for cooking gas. It is also used for the production of electricity.
- Biogas contains about 55% to 60% methane and the rest is carbon dioxide.
- Biogas is a fuel that is convenient to use, and in addition to this, very good manure is also produced as a side product of the process.
