Topics
Operating System
- Introduction to Operating System (OS)
- Idea of an Operating System
- Windows NT
- LINUX
- File Systems and Its types
- File Operations
- Access Methods and its types
- Allocation Methods
- Concepts Related to Process Management
- Concepts related to memory management
- Basics of Graphical User Interface (GUI)
- Access and Security Aspects of O.S.
Data Structures
C++ Programming
- Introduction to C++ Programming
- Idea Behind Object-Orientated Programming
- Object-orientated programming approach
- Object-Oriented Terms and Concepts
- Classes and Objects
- Constructors and Destructors
- Functions in C + +
- Arrays in C++
- Pointers in C++
- References in C++
- Strings in C++
- Inheritance
- Virtual functions and polymorphism
- Friends in C++
- Operator overloading and type conversions
- Files and Stream
HyperTex Markup Language (HTML)
- Services in O/S
- Overview of O/S
Operating System & Service of OS
Idea of an Operating System:
An operating system is a programme that interfaces between the user and computer hardware, providing an environment to execute programmes. Its primary goal is user convenience, and its secondary goal is efficient hardware utilisation.
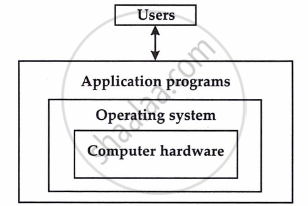
The figure below shows components of a computer system. Computer hardware is at the innermost level. The operating system is at an outer level to that of computer hardware. Application programmes are at the outer level of the operating system. Users form the outermost level.
Services in O.S. :
The operating system provides certain services to programs and to the users of those programs. There are three major categories of services:
- Information management (IM): Information management (IM) involves services for storing, retrieving, modifying, and removing information on various devices. It organizes information into directories and files, allocates sectors to files, controls access, and manages device operations.
- Process management (PM): In a multi-user operating system, multiple users run programs simultaneously. The OS tracks and schedules these processes, dispatching them one after another, creating the illusion that each user has full CPU control.
- Memory management (MM): Memory management tracks, allocates, and deallocates memory for processes, updating a free memory list based on program size.
Overview of operating system - Windows 98:
Microsoft developed the operating system referred as MS-DOS or PC-DOS for the first IBM personal computer. The features of Windows 98:
- Easier to use: Windows 98 is a single-user multitasking OS, supporting easy navigation, multiple monitors, USB hardware, and digital imaging devices.
- Faster: Windows and programs open faster, and maintenance wizard improves speed and efficiency. FAT 32 saves hard disk space.
- True web integration: Using the world wide web is easier and faster. The connection to the web is simple. Web pages can be viewed in any window.
- More entertaining: Windows 98 supports DVD and digital audio, you can play high quality digital movies and audio on the computer. The television broadcast can also be viewed on a computer.
