Topics
Number System
Number System(Consolidating the Sense of Numberness)
- Concept for Number System(Consolidating the Sense of Numberness)
- Consolidating the Sense of Numberness up to 5 Digits, Size, Estimation of Numbers, Identifying Smaller, Larger, Etc.
Sets
- Concept of Sets
- Representation of Sets
- Types of Sets: Finite/Infinite and Empty
- Cardinality of a Set
Estimation
- Concept of Estimation
- Estimation of Outcome of Number Operations
Numbers in India and International System (With Comparison)
- Numbers in Indian and Comparison
- Numbers in International Systems and Comparison
Place Value
Natural Numbers and Whole Numbers (Including Patterns)
Negative Numbers and Integers
- Negative and Positive Numbers
- Need for Negative Numbers
- Connection of Negative Numbers in Daily Life
- Representation of Negative Numbers on Number Line
- Ordering of Negative Numbers, Integers.
- Representation of Integers on the Number Line
- Operation of Addition and Subtraction of Integers
- Addition of Integers
- Comparison of Integers
- Concept for Ordering of Integers
Number Line
- Operation of Whole Numbers on Number Line
- Seeing Patterns for Operations on Numbers.
- Identifying And Formulating Rules for Operations on Numbers.
HCF and LCM
- Concept for HCF and LCM
- Prime Factorization for HCF and LCM
- Division Method for HCF and LCM
- Property HCF x LCM = Product of Two Numbers
Playing with Numbers
- Arranging the Objects in Rows and Columns
- Simplification of Expression by Using Brackets
- Factors and Multiples
- Concept of Even and Odd Number
- Concept for Co-prime Numbers, Prime Factorisation
Ratio and Proportion
Ratio
- Concept of Ratio
- Difference Between Fraction and Ratio.
Proportion (Including Word Problems)
- Proportion as Equality of Two Ratios
- Concept of Ratio
- Concept of Proportion
Unitary Method
- Concept for Unitary Method (With Only Direct Variation Implied)
Fractions
- Concept of Fraction as a Part of Whole
- Representation of Fractions (Pictorially and on Number Line).
- Concept for Fraction as a Division.
- Concept of Proper Fractions
- Concept of Equivalent Fractions
- Concept of Fractions
- Operations on Fractions (Avoid Large and Complicated Unnecessary Tasks). (Moving Towards Abstraction in Fractions).
Decimal Fractions
- The Decimal Number System
- Concept of Place Value
- Concept for Inter Conversion of Fractions
- Word Problems Involving Addition and Subtraction of Decimals (Two Operations Together on Money, Mass, Length and Temperature).
Percent (Percentage)
- Basic Concept of Percentage
- Idea of Percent as Fraction with 100 as Denominator
Idea of Speed, Distance and Time
- Relation Between Speed, Time and Distance
- Idea of Speed and Simple Daily Life Problems Related to Speed, Time and Distance
Algebra
Fundamental Concepts
- Fundamental Concepts for Algebra
- Introduction to Constants, Variable and Unknown Through Patterns
- Concept for Appropriate Word Problems and Generalisations
Fundamental Operations (Related to Algebraic Expressions)
- Operation on Algebraic Expression
- Algebra Terminology - Literal Numbers, Terms, Expressions, Factor, Coefficient, Polynomials, Degree, like and Unlike Terms
- Concept for Unknowns Through Examples with Simple Contexts (Single Operations)
Substitution (Including Use of Brackets as Grouping Symbols)
- Concept of Substitution
Framing Algebraic Expressions (Including Evaluation)
Simple (Linear) Equations (Including Word Problems)
- Concept of Simple (Linear) Equations (Including Word Problems)
- Linear Equation in One Variable
Geometry
Fundamental Concepts
- Introduction to Basic Concepts in Geometry
- Concept for Basic Geometrical Ideas (2 -d)
- Concept for Linkage with and Reflection in Everyday Experiences.
- Concept of Line
- Concept for Open and Closed Figures.
- Concept for Interior and Exterior of Closed Figures.
- Curvilinear and Linear Boundaries
- Concept of Angle
Angles (With Their Types)
- Types of Angles
- Measure of Angles
- Introduction to Lines and Angles
Properties of Angles and Lines (Including Parallel Lines)
- Concept of Angle
- Measure of Line Segment
- Pair of Lines – Intersecting and Perpendicular Lines, Parallel Lines
Triangles (Including Types, Properties and Constructions)
- Concept of Triangles
- Classification of Triangles (On the Basis of Sides, and of Angles)
Quadrilateral
- Concept of Quadrilaterals
- Interior and Exterior of a Quadrilateral.
- Concept of Quadrilaterals
Polygons
- Concept of Polygons
- Simple Polygons (Upto Octagons Regulars as Well as Non-regular).
- Sum of Angles of a Polynomial
- Sum of Exterior Angles of a Polynomial
- Regular Polynomial
The Circle
Revision Exercise Symmetry (Including Constructions on Symmetry)
- Concept of Revision Exercise Symmetry (Including Constructions on Symmetry)
- Concept of Reflection Symmetry
- Concept of Observation and Identification of 2-d Symmetrical Objects for Reflection Symmetry.
- Operation of Reflection (Taking Mirror Images) of Simple 2-d Objects
- Recognising Reflection Symmetry (Identifying Axes).
Recognition of Solids
- Concept of Recognition of Solids
- Identification of 3-d Shapes: Cubes, Cuboids, Cylinder, Sphere, Cone, Prism (Triangular and Square), Pyramid (Triangular and Square)
- Identification and Locating in the Surroundings.
- Faces, Edges and Vertices
- Nets for Building 3-d Shapes
- Faces, Edges and Vertices
Mensuration
Perimeter and Area of Plane Figures
- Concept of Perimeter
- Shapes of Different Kinds with the Same Perimeter.
- Concept of Area
- Conversion of Units (Mass, Time, Money, and Capacity) from to Smaller to Larger and Vice-versa
- Counter Examples to Different Misconcepts Related to Perimeter and Area.
- Perimeter of a Rectangle
- Deducing the Formula of the Perimeter for a Rectangle and Then a Square Through Pattern and Generalisation.
Data Handling
Data Handling (Including Pictograph and Bar Graph)
- Collection of Data to Examine a Hypothesis
- Collecting Data
- Concept of Pictograph
- Organisation of Data
Mean and Median
Introduction to Basic Concepts in Geometry
Geometry is the branch of mathematics that deals with the study of position, shape, size, and other properties of various figures. Geometrical terms such as point, line, plane, etc., carry the basic ideas for the development of geometry.
Fundamental Geometrical Concepts:
| Concept | Definition | Diagram |
| Point | A point is a mark of position. It has neither length nor width nor thickness; | 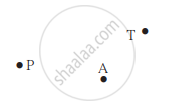 |
| Line | A line has only length. It has neither width nor thickness. | |
| Line Segment | A line segment is a part of a straight line. | 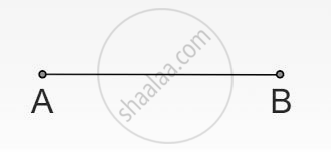 |
| Ray | A ray is a straight line that starts from a given fixed point and moves in the same direction |
 |
| Plane | It is a flat surface. A plane has length and width but no thickness. | 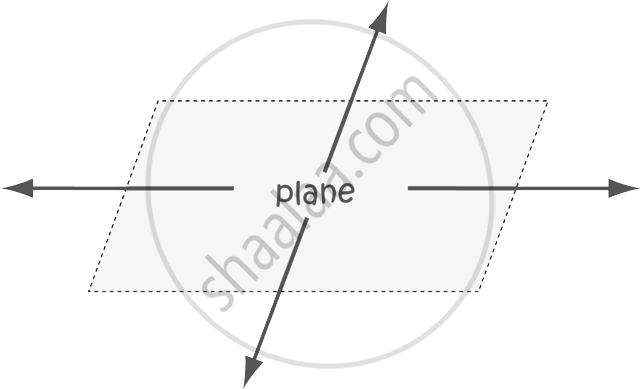 |
| Angle | Formed when two rays meet at a common point (vertex). | 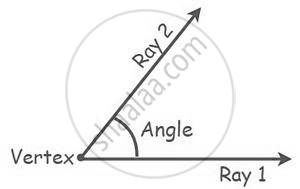 |
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
