Topics
Reproduction in Lower and Higher Plants
- Reproduction
- Mode of Reproduction in Plant
- Asexual Reproduction in Plant
- Vegetative Reproduction
- Natural Vegetative Reproduction
- Artificial Vegetative Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Structure and Events
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Stamen (Male Reproductive Unit)
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Microsporangium
- Structure of Microspore Or Pollen Grain
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Pistil (Female Reproductive Unit)
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Megasporangium
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Formation of Embryo Sac
- Pollination
- Self Pollination (Autogamy)
- Cross Pollination
- Agents of Pollination
- Outbreeding Devices
- Pollen Pistil Interaction
- Fertilization Process
- Post Fertilisation in Plant: Structures and Events
- Development of Endosperm
- Post Fertilization in Plant: Development of Embryo (Embryogeny)
- Formation of Seed and Fruit
- Apomixis
- Parthenocarpy
- Polyembryony
- Kinds of Pollination
Reproduction in Lower and Higher Animals
- Reproduction
- Mode of Reproduction in Animal
- Asexual Reproduction in Animal
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- Human Reproduction
- The Male Reproductive System
- The Female Reproductive System
- Menstrual Cycle (Ovarian Cycle)
- Gametogenesis
- Fertilization in Human
- Embryonic Development in Human
- Implantation in Human
- Pregnancy in Humans
- Placenta (Growth) in Human
- Parturition (Birth) in Human
- Lactation in Human
- Reproductive Health
- Population Stabilisation and Birth Control
- Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP)
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)
- Infertility
- Gastrulation in humans
Inheritance and Variation
- Heredity or Inheritance
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Genes and Genetic
- Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity
- Back Cross and Test Cross
- Deviations from Mendel’s Findings
- Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
- Chromosomes - The Carriers of Heredity
- Linkage and Crossing Over
- Autosomal Inheritance
- Sex Linked Inheritance
- Sex Determination
- Genetic Disorders
Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Its Structure
- The Genetic Material is a DNA
- Packaging of DNA Helix
- DNA Replication
- Protein Synthesis
- Regulation of Gene Expression
- Operon Concept
- Genomics
- Human Genome Project
- DNA Fingerprinting Technique
- Genetic Code
Origin and Evolution of Life
- Origin and Evolution of Universe and Earth
- Theories of Origin of Life
- Chemical Evolution of Life (Self-assembly Theory of the Origin of Life)
- Darwinism
- Mutation Theory
- Modern Synthetic Theory of Evolution
- Organic Evolution
- Hardy Weinberg’s Principle
- Adaptive Radiation
- Evidences for Biological Evolution
- Speciation
- Geological Time Scale
- Human Evolution
- Theories of Biological Evolution
Plant Water Relation
- Plant Water Relation
- Properties of Water
- Water absorbing organ
- Water Available to Roots for Absorption
- Means of Transport in Plants
- Concept of Imbibition
- Simple Diffusion
- Concept of Osmosis
- Osmotic Pressure
- Facilitated Diffusion
- Turgidity and Flaccidity (Plasmolysis)
- Active Transport
- Passive Transport
- Water Potential (ψ)
- Path of Water Across the Root
- Translocation of Water (Ascent of Sap)
- Transport of Mineral Ions
- Transport of Food
- Transpiration
- Types of Transpiration
- Structure of Stomatal Apparatus
- Significance of Transpiration
Plant Growth and Mineral Nutrition
- Plant Growth
- Phases of Plant Growth
- Conditions Necessary for Plant Growth
- Plant Growth Rate
- Plant Growth Curve
- Differentiation, De-differentiation, Re- Differentiation
- Plant Development
- Plant Plasticity
- Plant Hormones
- Types of Plant Hormones: Auxins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Gibberellins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Cytokinins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Ethylene
- Types of Plant Hormones: Abscisic Acid (ABA)
- Photoperiodism
- Vernalization (Yarovization)
- Plant Mineral Nutrition
- Nitrogen Cycle
Respiration and Circulation
- Respiration
- Organs of Respiratory Exchange
- Human Respiratory System
- Mechanism of respiration-Breathing
- Regulation of Breathing / Respiration
- Modified Respiratory Movements
- Disorders of Respiratory System
- Transportation in Living Organisms
- Circulation in Animals
- Types of Closed Circulation
- Blood Circulatory System in Human
- Composition of Blood: Plasma (The Liquid Portion of Blood)
- Composition of Blood: Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
- Composition of Blood: White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
- Composition of Blood: Blood Platelets (Thrombocytes)
- Function of Platelets - Clotting of Blood (Coagulation)
- Human Heart
- Working mechanism of human heart
- Blood Vessels
- Blood Pressure (B.P.)
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Lymph and Lymphatic System
- Mechanism of respiration - Internal respiration
- Mechanism of respiration - External respiration
- Mechanism of respiration - Cellular respiration
Control and Co-ordination
- Control and Co-ordination
- Nervous System in Hydra
- Nervous System in Planaria (Flatworm)
- Neural Tissue
- Neuron (Or Nerve Cell) and Its Types
- Neuroglial Cells (Or Glial Cells)
- Human Nervous System
- Central Nervous System (CNS)
- The Human Brain - Forebrain
- The Spinal Cord
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- Sensory Receptors
- Human Eye
- Human Ear
- Disorders of Nervous System
- Chemical Coordination
- Human Endocrine System
- The Hypothalamus
- Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis Gland
- The Pineal Gland
- Thyroid Gland
- Parathyroid Gland
- Thymus Gland
- Adrenal Gland (Suprarenal Gland)
- Pancreas (Islets of Langerhans)
- Reproductive Glands (Gonads)
- Synapse - Properties of nerve fibres
- Synapse - Types of synapse
- Transmission of nerve impulse
- Generation of nerve impulse
- Reflex Action
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
- Diffuse Endocrine Glands
Human Health and Diseases
- Defence System in Our Body: Immune System
- Immunity
- Types of Immunity
- Vaccination and Immunization
- Structure of Antibody
- Disease
- Protozoan Diseases
- Helminthic Diseases
- Bacterial Diseases
- Viral Diseases
- Fungal Diseases
- Vector Borne Diseases
- Cancer
- Adolescence
- Addiction
- Drug Abuse
Enhancement of Food Production
- Improvement in Food Production
- Plant Breeding
- Tissue Culture
- Single Cell Protein (SCP)
- Biofortification
- Animal Husbandry (Livestock)
- Animal Breeding
- Dairy Farming
- Poultry Farming
- Apiculture (Bee Farming)
- Pisciculture (Fish Farming)
- Sericulture
- Lac Culture
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Microbes in Industrial Production
- Microbes in Sewage Treatment
- Microbes in Energy Generation
- Microbes as Biocontrol Agents
- Microbes as Biofertilizers
Biotechnology
- Biotechnology
- Process and Principles of Biotechnology
- Methodology for rDNA Technology
- Commercial Applications of Biotechnology
- Bioethics
- Effects of Biotechnology on the Environment
- Biopatent and Biopiracy
- Transgenic Plants
- Transgenic animals
- Effects of Biotechnology on Human Health
- Tools and techniques for gene cloning/ rDNA technology
Organisms and Populations
- Organisms and the Environment Around
- Habitat
- Niche
- Structure and function of an Ecosystem
- Adaptations and Its Types
- Population
- Population Interactions
- Organisms and Populations
Ecosystems and Energy Flow
- Ecosystem
- Structure and function of an Ecosystem
- Concept of Energy Flow in an Ecosystem
- Classification of Animal
- Trophic Level
- Food Chain
- Food Web
- Ecological Pyramids
- Nutrient Cycles
- Ecological Succession
- Ecosystem Services
- Productivity
- Decomposition
- Phosphorus Cycle
- Carbon Cycle
Biodiversity, Conservation and Environmental Issues
- Biodiversity
- Levels of Biodiversity
- Patterns of Biodiversity
- Biodiversity Current Scenario
- Loss of Biodiversity
- Conservation of Wildlife
- Biological Diversity Act, 2002
- Environmental Issues
- Air Pollution and Its Causes
- Noise Pollution
- Water Pollution and Its Causes
- Green House Effect
- Preventive Measures of Green House Effect
- Global Warming
- Preventive Measures of Global Warming
- Ozone Layer Depletion
- Deforestation and Its Causes
- Mission Harit Maharashtra
- Conservation of Biodiversity
Excretion and Osmoregulation
- Modes of Excretion: Ammonotelism, Ureotelism, and Uricotelism
- Human Excretory System
- Function of the Kidney - “Production of Urine”
- Regulation of Kidney Function
- Common Disorders of the Urinary System
Human Reproduction
- Reproductive and Child Health Care (RCH) Programme
- Goals of RCH Programmes
Notes
Introduction of reproductive health:
- The term 'Reproductive health' simply refers to healthy reproductive organs with normal functions. However, it has a broader perspective and includes the emotional and social aspects of reproduction also.
- According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), reproductive health means total well-being in all aspects of reproduction, i.e., physical, emotional, behavioural, and social.
- Therefore, a society with people having physically and functionally normal reproductive organs and normal emotional and behavioural interactions among them in all sex-related aspects might be called reproductively healthy.
Goals of RCH Programmes:
- To create awareness among people about various aspects related to reproduction.
- To provide the facilities to people to understand and build up reproductive health.
- To provide support for building up a reproductively healthy society.
- To bring about a change mainly in three critical health indicators i.e. reducing total infertility rate, infant mortality rate and maternal mortality rate.
The goals of RCH can be achieved by the following ways:
- By introduction of sex education in schools. Proper information about safe and hygenic sexual practices, sexually transmitted diseases (STD, AIDS), problems related to adolescence and proper information about reproductive organs.
- By educating the younger generation about birth control measures, pre-natal care of pregnant woman and post-natal care of the mother and child, importance of breast feeding.
- By creating awareness about statutory ban on amniocentesis for sex determination.By creating awareness about child immunization programmes.
REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH:-
Reproductive health means a total well being in all aspects of reproductive i.e. physical emotional, social and behavioural.
Sexually transmitted disease (STDs):-
-Many disease can be sexually transmitted such as:
(i) Bacterial: Gonorrhoea and syphilis
(ii) Viral: Warts and HIV- AIDS
-Use of condom prevents these infections to some extent.
-Contraception: It is the avoidance of pregnancy, can be achieved by preventing the fertilisation of ova.
Methods of contraception
(i) Physical barrier:
-To prevent union of egg and sperm
-Use of condoms, cervical caps and diaphragm.
(ii) Chemical methods:
-Use of oral pills
-These change hormonal balance of body so that eggs are not released
-May have side effects
(iii)Intrauterine contraceptive device. (IUCD)
-Copper – T or loop is placed in the uterus to prevent pregnancy
(iv)Surgical Methods:
-In males the vas deferens is blocked to prevent sperm transfer called vasectomy.
-In females the fallopian tube is blocked to prevent egg transfer called tubectomy.
Female Foeticide:
-The practice of killing a female child inside the womb is called female foeticide
-For a healthy society, a balanced sex ratio is needed that can be achieved by educating people to avoid malpractices like female foeticide and prenatal sex determination.
-Pernatal sex determination is a legal offence in our country so as to maintain a balanced sex ratio.
Reproductive health - Problems and Strategies:
- India was amongst the first countries in the world to initiate action plans and programmes at a national level to attain total reproductive health as a social goal. Family planning measures were initiated in 1951 in India. The goal was to attain total reproductive health. These measures were periodically evaluated.
- Reproductive and Child Health Care (RCH) Programs are being operated with the aim of creating awareness among people about various reproduction related aspects and providing facilities and support for building a reproductively healthy society.
Strategies to build a reproductively healthy society:
- Governmental and non-governmental agencies should use media-both print and audio-visual, to create awareness programs.
- Responsible adults, parents, teachers, close relatives, and friends should provide correct information and be willing to open dialogues with young adults and children to sensitize them about reproductive health.
- Introduction of sex education in schools should also be encouraged to provide the right information to the young so as to discourage children from believing in myths and having misconceptions about sex-related aspects.
- Proper information about reproductive organs, adolescence and related changes, safe and hygienic sexual practices, sexually transmitted diseases (STD), AIDS, etc., would help people, especially those in the adolescent age group to lead a reproductively healthy life.
- Educating people, especially fertile couples and those in the marriageable age group, about available birth control options, care of pregnant mothers, post-natal care of the mother and child, the importance of breastfeeding, equal opportunities for the male and the female child, etc., would address the importance of bringing up socially conscious healthy families of the desired size.
- Awareness of problems due to uncontrolled population growth, social evils like sex abuse and sex-related crimes, etc., need to be created to enable people to think and take up necessary steps to prevent them and thereby build up a socially responsible and healthy society.
- Successful implementation of various action plans to attain reproductive health requires strong infrastructural facilities, professional expertise and material support. These are essential to provide medical assistance and care to people in reproduction-related problems like pregnancy, delivery, STDs, abortions, contraception, menstrual problems, infertility, etc.
- Implementation of better techniques and new strategies from time to time are also required to provide more efficient care and assistance to people.
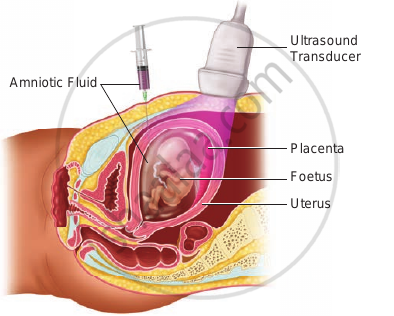
- Statutory ban on amniocentesis for sex-determination to legally check the increasing menace of female foeticides, massive child immunization, etc., are some programmes that merit mention in this connection. In amniocentesis, some of the amniotic fluid of the developing foetus is taken to analyze the fetal cells and dissolved substances. This procedure is used to test for the presence of certain genetic disorders such as, down syndrome, haemoplilia, sickle-cell anemia, etc., to determine the survivability of the foetus.
- Research on various reproduction-related areas is encouraged and supported by governmental and non-governmental agencies to find out new methods and/or to improve upon the existing ones. ‘Saheli’– a new oral contraceptive for females - was developed by scientists at Central Drug Research Institute (CDRI) in Lucknow, India.
‘Saheli’– a new oral contraceptive pills
Better awareness about sex-related matters, increased number of medically assisted deliveries, and better post-natal care leading to decreased maternal and infant mortality rates, increased number of couples with small families, better detection and cure of STDs, and overall increased medical facilities for all sex-related problems, etc. all indicate improved reproductive health of the society.
Amniocentesis (or Prenatal Diagnostic Tests):
Amniocentesis is a foetal sex and disorder determination test based on the chromosomal pattern of the embryo’s cells in the amniotic fluid surrounding the developing embryo.
|
Amniocentesis |
Procedure: Amniotic fluid contains cells from the skin of the foetus and others sources. These cells can be used to determine the sex of the infant, identify some abnormalities in the number of chromosomes and to detect certain biochemicals and enzymatic abnormalities. If it is established that the child is likely to suffer from a serious incurable congenital defect, the mother should get the foetus aborted.
Misuse: It is being used to kill the normal female foetus; hence it is legally banned to avoid female foeticide.
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS): CVS is a prenatal test that involves taking a sample of the placental tissue to test for chromosomal abnormalities.
Video Tutorials
Shaalaa.com | Reproductive health I
Related QuestionsVIEW ALL [128]
Given below are four aspects of Reproductive Health in Column A and their related information in Column B:
| Column A | Column B | ||
| S. No. | Terms used in Reproductive Health | S. No. | Significant information |
| (A) | MTP | (i) | Analysing fetal cells from amniotic fluid of the foetus |
| (B) | Amniocentesis | (ii) | Legalised in 1971 |
| (C) | Saheli | (iii) | Programme initiated in 1951 |
| (D) | Family Planning | (iv) | Non-steroidal oral Planning contraceptive |
Select the correct match from the following options: