Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
1 kg of ice at 0°C is mixed with 1 kg of steam at 100°C. What will be the composition of the system when thermal equilibrium is reached? Latent heat of fusion of ice = 3.36 × 103 J kg−1 and latent heat of vaporization of water = 2.26 × 106 J kg−1.
उत्तर
Given:-
Amount of ice at 0oC = 1 kg
Amount of steam at 100oC = 1 kg
Latent heat of fusion of ice = 3.36 × 103 J kg−1
Latent heat of vapourisation of water = 2.26 × 106 J kg−1
We can observe that the latent heat of fusion of ice (3.36 × 105 J kg−1) is smaller that latent heat of vapouisation of water (2.26 × 106 ). Therefore, ice will first change into water as less heat is required for this and there will be equilibrium between steam and water.
Heat absorbed by the ice when it changes into water (Q1) = 1×(3.36 × 105) J
Heat absorbed by the water formed to change its temperature from 0oC to 100oC (Q2) = 1 × 4200 × 100 = 4.2 × 105 J
Total heat absorbed by the ice to raise the temperature to 100°C, Q = Q1+Q2 = 3.36 × 105+ 4.2 × 105 = (3.36 + 4.2) × 105 = 7.56 × 105 J
The heat required to change ice into water at 100oC is supplied by the steam. This heat will be released by the steam and will then change into water.
If all the steam gets converted into water, heat released by steam, Q' = 1 ×( 2.26 × 106) J = 2.26 × 106 J
Amount of heat released is more than that required by the ice to get converted into water at 100oC. Thus,
Extra heat = Q − Q'
= (2.26 − 0.756) × 106
= 1.506 × 106
Let the mass of steam that is condensed into water be m. Thus,
`m=(7.56xx10^5)/(2.26xx10^6)=0.335kg=335gm`
Total amount of water at 100°C = 1000 + 335 = 1335 g =1.335 g
Steam left = 1− 0.335 = 0.665 kg = 665 gm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
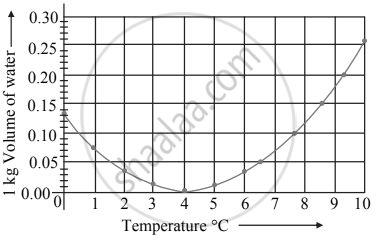
Observe the following graph. Considering the change in volume of water as its temperature is raised from 0°C, discuss the difference in the behaviour of water and other substances. What is this behaviour of water called?

On a winter day the temperature of the tap water is 20°C whereas the room temperature is 5°C. Water is stored in a tank of capacity 0.5 m3 for household use. If it were possible to use the heat liberated by the water to lift a 10 kg mass vertically, how high can it be lifted as the water comes to the room temperature? Take g = 10 m s−2.
A calorimeter contains 50 g of water at 50°C. The temperature falls to 45°C in 10 minutes. When the calorimeter contains 100 g of water at 50°C, it takes 18 minutes for the temperature to become 45°C. Find the water equivalent of the calorimeter.
What do you mean by the anomalous expansion of water?
Explain the following
A hollow glass sphere which floats with its entire volume submerged in water at 4°C, sinks when water is heated above 4°C.
A deep pond of water has its top layer frozen. What will be the likely temperature of water layer just in contact with ice?
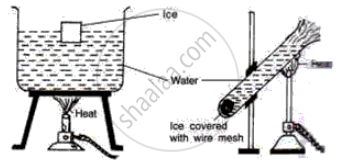
Study the following diagrams and write down your observations.
Observe the given graph and answer the following questions:
- Name the process represented in the figure.
- At what temperature does this process take place?
_______ apparatus is used to study the anomalous behaviour of water.
Write the name.
The instrument used to study anomalous behaviour of water.
Write scientific reason.
Fish can survive even in frozen ponds in cold regions.
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of Hope’s apparatus.
A graph between the volume and temperature of water is shown. Explain the anomalous behaviour of water.

