Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A 5 V battery is connected to two 20 Ω resistors which are joined together in series.
(a) Draw a circuit diagram to represent this. Add an arrow to indicate the direction of conventional current flow in the circuit.
(b) What is the effective resistance of the two resistors?
(c) Calculate the current that flows from the battery?
(d) What is the p.d. across each resistor?
उत्तर
Circuit diagram

Since two resistors of 20 Ω are connected in series, the effective resistance will be
R = R1+ R2
Here, R1=20 Ω,
R2 =20 Ω
Therefore,
R = 20 Ω + 20 Ω = 40 Ω
The effective resistance of the two resistors, R= 40 Ω
(c) The current that flows from the battery,
I = V / R
I = 5 / 40
I = 0.125 A
(d) The p.d. across the 20 Ω resistor, V=`IxxR`
V = 20 x 0.125 V
V = 2.5 V
Similarly, the potential difference across the second 20 Ω resistor is equal to 2.5 V.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How many microamperes are there in 1 ampere?
Which effect of current is utilised in the working of an electric fuse?
Calculate the equivalent resistance between A and B in the adjacent diagram.
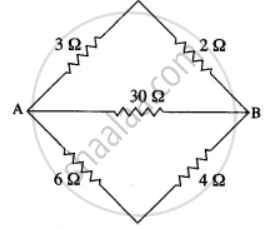
Define the following:
Electromotive force
The circuit diagram (Fig.) shows a battery of e.m.f. 6 volts and internal
resistance of 0.8 Ω oonnected in series. Find the
(a) Current reoorded by the ammeter,
(b) P.d. across the terminals of the resistor B,
( c) Current passing through each of the resistors B, C and D, and
( d) P.d. across the terminals of the battery.
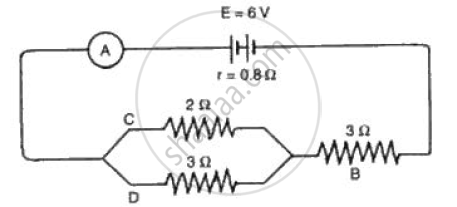
If the potential differences between two parts of a thundercloud is 10s V,
what is the amount of energy given up during the passage of 20 coulombs?
(a)2x10-7J
(b)200J
(c)Sx106 j
(d)2x 109J
(e)2x 1010 J
State the S.I. units of electrical power.
What is the speed of electric current?
