Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A bag contains 5 white balls and some blue balls. If the probability of drawing a blue ball is double that of a white ball, determine the number of blue balls in the bag
उत्तर
Let the number of blue balls be x.
Number of white balls = 5
∴ Total number of balls = (x + 5)
P(blue ball is drawn) = `x/(x + 5)`
P(white ball is drawn) = `5/(x + 5)`
According to the given condition, the probability of drawing a blue ball is double that of a white ball.
∴ P(blue ball is drawn) = 2 × P(white ball is drawn)
∴ `x/(x +5) = 2 xx 5/(x + 5)`
∴ x(x + 5) = 10(x + 5)
∴ x2 + 5x = 10x + 50
∴ x2 – 5x – 50 = 0
∴ x2 – 10x + 5x – 50 = 0
∴ x(x – 10) + 5(x – 10) = 0
∴ (x – 10)(x + 5) = 0
∴ x – 10 = 0 or x + 5 = 0
∴ x = 10 or x = – 5
But, number of balls cannot be negative.
∴ x = 10
∴ The number of blue balls in the bag is 10.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The six faces of a die are marked
The event M is getting a vowel on the upper face of the die when it is tossed. Complete the following activity and find the probability of the event.
`"S" = {square}`
`"n"("S") = square`
`"M" = {square}`
`"n"("M") =square`
`"P"("M") = square/square=square`
If one die is rolled, then find the probability of the following event by completing the activity.
Event A: The number on the upper face is prime.
Activity: Let ‘S’ be the sample space.
S = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
∴ n(S) = 6
Event A: Prime number on the upper face.
A = {`square`}
∴ n(A) = 3
P(A) = `square/(n(S))` .....[Formula]
= `square/6`
∴ P(A) = `1/square`
A card is drawn from a well shuffled pack of 52 playing cards. Find the probability of the event, the card drawn is a red card.
Activity: Let ‘S’ be the sample space.
∴ n(S) = 52
Event A: Card drawn is a red card.
∴ Total red cards = `square` hearts + 13 diamonds
∴ n(A) = `square`
∴ P(A) = `square/(n("S"))` ......[Formula]
P(A) = `26/52`
P(A) = `square`
If two coins are tossed, find the probability of event getting head on both the coins
If three coins are tossed simultaneously, find the probability of the event to get no head
If three coins are tossed simultaneously, find the probability of the following events
Event A: To get no head.
A box contains 36 cards, bearing only one number from 1 to 36 on each. If one card is drawn at random, find the probability of an event that the card drawn bears, a complete square number
A box contains 36 cards, bearing only one number from 1 to 36 on each. If one card is drawn at random, find the probability of an event that the card drawn bears, a prime number
A box contains 36 cards, bearing only one number from 1 to 36 on each. If one card is drawn at random, find the probability of an event that the card drawn bears, a number divisible by 3
A missing helicopter is reported to have crashed somewhere in the rectangular region shown in the figure. What is the probability that it crashed inside the lake shown in the figure?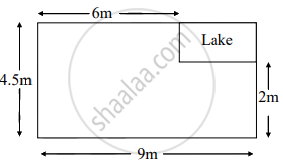
A handbag contained fifty ten rupees note, thirty-five fifty rupees note and fifteen hundred rupee note. One note is drawn from a handbag. What is the probability of getting:
Ten rupees note
A handbag contained fifty ten rupees note, thirty-five fifty rupees note and fifteen hundred rupees note. One note is drawn from a handbag. What is the probability of getting:
Fifty rupees note
Let E be an event and P(E) = `6/7`, then find the value of P(not E).
The probability that a relation R from {x, y} to {x, y} is both symmetric and transitive, is equal to ______.
A five digit number is formed by the digits 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 without repetition. If the probability that the number formed is divisible by 4, is P, then 5P is ______.
A coin is tossed twice and the four possible outcomes are assumed to be equally likely. If A is the event, 'both head and tail have appeared' and B the event,' at most one tail is observed,' then the value of P(B/A) is ______.
A two digit number is formed with digits 2, 3, 5, 7, 9 without repetition. What is the probability of the following events?
Event A : The number formed is an odd number.
Event B : The number formed is a multiple of 5.
One coin and a die are thrown simultaneously. Find the probability of the following event:
Event A: To get a head and a prime number.
