Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A beaker contains a liquid of density ‘ρ’ up to height ‘h’ such that ‘PA’ is atmospheric pressure and ‘g’ is the acceleration due to gravity. Answer the following questions:
- What is the pressure on the free surface of the liquid?
- What is the pressure on the base of the beaker?
- What is the lateral pressure at the base on the inner walls of the beaker?
उत्तर
a. Pressure on the free surface of the liquid is equal to the atmospheric pressure (Pa).
b. Consider a liquid contained in a beaker, such that ‘ p’ is the density of the liquid.
Consider a point B at the base of liquid and the liquid column of the area of cross-section ‘a’ around it, such that ‘h’ is the height of the liquid column as shown in the figure
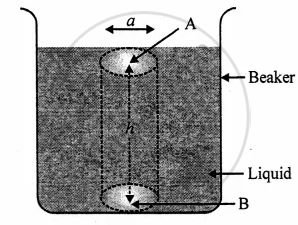
∴ Volume of the imaginary column of liquids = area of cross-section × length = ah
∴ Mass of liquid column = Volume × density
= V × ρ = a.h.ρ
∴ Weight of liquid column =mass × g = mg
= a.h.ρ.g.
∴Thrust exerted by liquid column on the base of the breaker
= a.h.ρ.g.
∴ Pressure due to the liquid column
P = `"Force"/"Area"="F"/"a"="ahρg"/"a"`
P = h.ρ.g.
So, pressure on the base of beaker = hρg
∴ Total pressure at the base of beaker = Atmospheric pressure + hρg
= Pa + hρg
c. Also lateral pressure at the base on the inner walls of beaker = Pa + hρg
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A body while floating sinks deeper in a liquid of low density than in a liquid of high density.
The buoyant force experienced by a body when floating in saltwater is ....... to or same that of when floating in pure water.
Define the term relative density of a substance.
Which of the following will sink or float on water? (Density of water = 1 g Cm-3)
body C having density 1100 kg m-3
How is the unit bar related to the S.I. unit pascal?
State whether thrust is a scalar or vector?
A tall vertical cylinder filled with water is kept on a horizontal table top. Two small holes A and B are made on the wall of the cylinder, A near the middle and B just Below the free surface of water. State and explain your observation.
A metal solid cylinder tied to a thread is hanging from the hook of a spring balance. The cylinder is gradually immersed into the water contained in a jar. What changes do you expect in the readings of the spring balance? Explain your answer.
The upward force that is caused due to the pressure difference in liquid (or fluid) is called ______.
The center of gravity of the floating body and the center of buoyance are in the same ______ line.
