Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A block of mass 1 kg is pushed up a surface inclined to horizontal at an angle of 30° by a force of 10 N parallel to the inclined surface (Figure). The coefficient of friction between block and the incline is 0.1. If the block is pushed up by 10 m along the incline, calulate
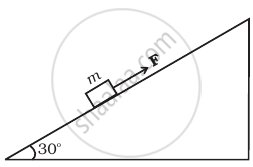
- work done against gravity
- work done against force of friction
- increase in potential energy
- increase in kinetic energy
- work done by applied force.
उत्तर
Consider the adjacent diagram the block is pushed up by applying a force F.
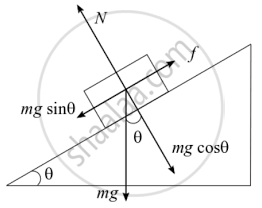
Normal reaction (N) and frictional force (f) is shown.
Given, mass = m = 1 kg, θ = 30°
F = 10 N, μ = 0.1 and s = distance moved by the block along the inclined plane = 10 m
a. Work done against gravity = Increase in PE of the block
= mg × Vertical distance travelled
= mg × s(sin θ) = (mgs) sin θ
= 1 × 10 × 10 × sin 30° = 50 j ....(∵ g ≤ 10 m/s2)
b. Work done against friction
wf = f × s = μN × s = μ mg cos θ × s
= 0.1 × 1 × 10 × cos 30° × 10
= 10 × 0.866
= 8.66 J
c. Increase in PE = mgh = mg (s sin θ)
= 1 × 10 × 10 × sin 30°
= `100 xx 1/2`
= 50 J
d. By the work-energy theorem, we know that work done by all the forces = change in KE
(W) = ΔK
ΔK = Wg + Wf + Wf
⇒ = – mgh – fs + FS
= – 50 – 8.66 + 10 × 10
= – 50 – 8.66
= 41.34 J
e. Work done by the applied force, F = FS
= (10)(10)
= 100 J
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State if the following statement is true or false. Give a reason for your answer.
Work done in the motion of a body over a closed loop is zero for every force in nature.
A body of mass m is placed on a table. The earth is pulling the body with a force mg. Taking this force to be the action what is the reaction?
When you hold a pen and write on your notebook, what kind of force is exerted by you on the pen? By the pen on the notebook? By you on the notebook?
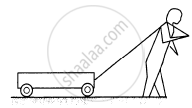
Figure shows a boy pulling a wagon on a road. List as many forces as you can which are relevant with this figure. Find the pairs of forces connected by Newton's third law of motion.
The sum of all electromagnetic forces between different particles of a system of charged particles is zero
Which of the following systems may be adequately described by classical physics ?
(a) motion of a cricket ball
(b) motion of a dust particle
(c) a hydrogen atom
(d) a neutron changing to a proton.
Two spherical bodies, each of mass 50 kg, are placed at a separation of 20 cm. Equal charges are placed on the bodies and it is found that the force of Coulomb repulsion equals the gravitational attraction in magnitude. Find the magnitude of the charge placed on either body.
The force with which the earth attracts an object is called the weight of the object. Calculate the weight of the moon from the following data : The universal constant of gravitation G = 6.67 × 11−11 N−m2/kg2, mass of the moon = 7.36 × 1022 kg, mass of the earth = 6 × 1024 kg and the distance between the earth and the moon = 3.8 × 105 km.
A particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude which is always perpendicular to the velocity of the plane. The motion of the particle takes place in a plane. It follows that
(a) its velocity is constant
(b) its acceleration is constant
(c) its kinetic energy is constant
(d) it moves in a circular path.
A body is displaced from (0, 0) to (1 m, 1 m) along the path x = y by a force F = (x2`hat"J"` + y`hat"i"`)N. The work done by this force will be:
