Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A body of mass 10 kg is acted upon by two perpendicular forces, 6 N and 8 N. The resultant acceleration of the body is ______.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
उत्तर
a and c
Explanation:
Consider the adjacent diagram
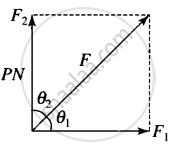
Given, mass = m = 10 kg
F1 = 6 N, F2 = 8 N
Resultant force = F = `sqrt(F_1^2 + F_2^2)`
= `sqrt(36 + 64)`
= 10 N
a = `F/m = 10/10` = 1 m/s2; along R.
Let θ1 be the angle between R and F1.
tan θ1 = `8/6 = 4/3`
θ1 = `tan^-1 (4/3)` w.r.t. F1 = 6 N
Let θ2 be the angle between F and F2.
tan θ2 = `6/8 = 3/4`
θ2 = `tan^-1 (3/4)` w.r.t. F2 = 8 N
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Is it possible for a particle to describe a curved path if no force acts on it? Does your answer depend on the frame of reference chosen to view the particle?
It is sometimes heard that the inertial frame of reference is only an ideal concept and no such inertial frame actually exists. Comment.
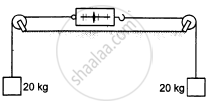
The figure shows a light spring balance connected to two blocks of mass 20 kg each. The graduations in the balance measure the tension in the spring. (a) What is the reading of the balance? (b) Will the reading change if the balance is heavy, say 2.0 kg? (c) What will happen if the spring is light but the blocks have unequal masses?
A plumb bob is hung from the ceiling of a train compartment. If the train moves with an acceleration 'a' along a straight horizontal track , the string supporting the bob makes an angle tan−1 (a/g) with the normal to the ceiling. Suppose the train moves on an inclined straight track with uniform velocity. If the angle of incline is tan−1 (a/g), the string again makes the same angle with the normal to the ceiling. Can a person sitting inside the compartment tell by looking at the plumb line whether the train is accelerating on a horizontal straight track or moving on an incline? If yes, how? If not, then suggest a method to do so.
Three rigid rods are joined to form an equilateral triangle ABC of side 1 m. Three particles carrying charges 20 μC each are attached to the vertices of the triangle. The whole system is at rest in an inertial frame. The magnitude of the resultant force on the charged particle at A is.
A block of mass 2 kg placed on a long frictionless horizontal table is pulled horizontally by a constant force F. It is found to move 10 m in the first seconds. Find the magnitude of F.
An object of mass 2 kg is sliding with a constant velocity of 4 m/s on a frictionless horizontal table. The force required to keep this object moving with the same velocity is :
State Newton's first law of motion.
Define one Newton.
This question has Statement 1 and Statement 2. Of the four choices given after the Statements, choose the one that best describes the two Statements.
Statement 1: If you push on a cart being pulled by a horse so that it does not move, the cart pushes you back with an equal and opposite force.
Statement 2: The cart does not move because the force described in statement 1 cancel each other.
