Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A body of mass 10 kg is acted upon by two perpendicular forces, 6 N and 8 N. The resultant acceleration of the body is ______.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
Solution
a and c
Explanation:
Consider the adjacent diagram
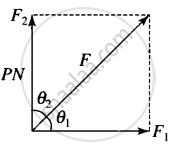
Given, mass = m = 10 kg
F1 = 6 N, F2 = 8 N
Resultant force = F = `sqrt(F_1^2 + F_2^2)`
= `sqrt(36 + 64)`
= 10 N
a = `F/m = 10/10` = 1 m/s2; along R.
Let θ1 be the angle between R and F1.
tan θ1 = `8/6 = 4/3`
θ1 = `tan^-1 (4/3)` w.r.t. F1 = 6 N
Let θ2 be the angle between F and F2.
tan θ2 = `6/8 = 3/4`
θ2 = `tan^-1 (3/4)` w.r.t. F2 = 8 N
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name the physical quantity whose unit is ‘newton’.
Three rigid rods are joined to form an equilateral triangle ABC of side 1 m. Three particles carrying charges 20 μC each are attached to the vertices of the triangle. The whole system is at rest in an inertial frame. The magnitude of the resultant force on the charged particle at A is.
A particle is observed from two frames S1 and S2. Frame S2 moves with respect to S1with an acceleration a. Let F1 and F2 be the pseudo forces on the particle when seen from S1 and S2, respectively. Which of the following is not possible?
A block of 2 kg is suspended from a ceiling by a massless spring of spring constant k = 100 N/m. What is the elongation of the spring? If another 1 kg is added to the block, what would be the further elongation?
'When a hanging carpet is beaten with a stick, the dust particles start coming out of it'. This phenomenon can be best explained by making use of :
An object of mass 2 kg is sliding with a constant velocity of 4 m/s on a frictionless horizontal table. The force required to keep this object moving with the same velocity is :
State Newton's first law of motion.
How does Newton's second law of motion differ from the first law of motion?
A man riding on a car has ___________ Inertia.
If a 5 N and a 15 N forces are acting opposite to one another. Find the resultant force and the direction of action of the resultant force.
