Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Three rigid rods are joined to form an equilateral triangle ABC of side 1 m. Three particles carrying charges 20 μC each are attached to the vertices of the triangle. The whole system is at rest in an inertial frame. The magnitude of the resultant force on the charged particle at A is.
Options
zero
3.6 N
3.6`sqrt3` N
7.2 N
Solution
zero
Using, Fnet = ma,
a = 0 ⇒ Fnet = 0
As the whole system is at rest, the resultant force on the charged particle at A is zero.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A batsman hits a cricket ball which then rolls on a level ground. After covering a short distance, the ball comes to rest. The ball slows to a stop because ______.
If the speed of the stone is increased beyond the maximum permissible value, and the string breaks suddenly, which of the following correctly describes the trajectory of the stone after the string breaks?
What is the other name of Newton’s first law of motion ?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
Newton’s first law of motion is also called Galileo’s law of ………………………
A moving bicycle comes to rest after sometime if we stop pedalling it. But Newton’s first law of motion says that a moving body should continue to move for ever, unless some external force acts on it. How do you explain the bicycle case ?
Name the law involved in the following situation :
if there were no friction and no air resistance, then a moving bicycle would go on moving for ever.
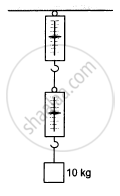
A block of mass 10 kg is suspended from two light spring balances, as shown in the following figure.
Neglect the effect of rotation of the earth. Suppose the earth suddenly stops attracting objects placed near its surface. A person standing on the surface of the earth will.
A reference frame attached to the earth
(a) is an inertial frame by definition
(b) cannot be an inertial frame because the earth is revolving around the sun
(c) is an inertial frame because Newton's laws are applicable in this frame
(d) cannot be an inertial frame because the earth is rotating about its axis.
How does Newton's second law of motion differ from the first law of motion?
What do you mean by inertia of motion?
Give one example each of inertia of rest and inertia of motion.
Define one Newton.
Give two examples of the following:
Inertia of motion
Match the following
| Column I | Column II |
| Newton’s I law | propulsion of a rocket |
| Newton’s II law | Stable equilibrium of a body |
| Newton’s III law | Law of force |
| Law of conservation of linear momentum | Flying nature of bird |
A car of mass m starts from rest and acquires a velocity along east `v = vhati (v > 0)` in two seconds. Assuming the car moves with uniform acceleration, the force exerted on the car is ______.
A body of mass 10 kg is acted upon by two perpendicular forces, 6 N and 8 N. The resultant acceleration of the body is ______.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
Block A of weight 100 N rests on a frictionless inclined plane of slope angle 30° (figure). A flexible cord attached to A passes over a frictonless pulley and is connected to block B of weight W. Find the weight W for which the system is in equilibrium.

A force F is applied to the initially stationary cart. The variation of force with time is shown in the figure. The speed of the cart at t = 5 sec is ______.

A balloon has mass of 10 g in air. The air escapes from the balloon at a uniform rate with velocity 4.5 cm/s. If the balloon shrinks in 5 s completely. Then, the average force acting on that balloon will be (in dyne).
