Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A block of mass 10 kg is suspended from two light spring balances, as shown in the following figure.
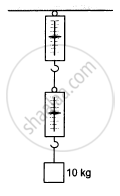
Options
Both the scales will read 10 kg.
Both the scales will read 5 kg.
The upper scale will read 10 kg and the lower zero.
The readings may be anything but their sums will be 10 kg.
Solution
Both the scales will read 10 kg.
From the free-body diagram
K1x1 = mg = 10 x 9.8 = 98 N
K2x2 = K1x1
So, K1x1 = K2x2 = 98 N
Therefore, both the spring balances will read the same mass, i.e. 10 kg.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If the speed of the stone is increased beyond the maximum permissible value, and the string breaks suddenly, which of the following correctly describes the trajectory of the stone after the string breaks?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
Newton’s first law of motion is also called Galileo’s law of ………………………
A moving bicycle comes to rest after sometime if we stop pedalling it. But Newton’s first law of motion says that a moving body should continue to move for ever, unless some external force acts on it. How do you explain the bicycle case ?
Consider a book lying on a table. The weight of the book and the normal force by the table in the book are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. Is this an example of Newton's third law?
A plumb bob is hung from the ceiling of a train compartment. If the train moves with an acceleration 'a' along a straight horizontal track , the string supporting the bob makes an angle tan−1 (a/g) with the normal to the ceiling. Suppose the train moves on an inclined straight track with uniform velocity. If the angle of incline is tan−1 (a/g), the string again makes the same angle with the normal to the ceiling. Can a person sitting inside the compartment tell by looking at the plumb line whether the train is accelerating on a horizontal straight track or moving on an incline? If yes, how? If not, then suggest a method to do so.
Neglect the effect of rotation of the earth. Suppose the earth suddenly stops attracting objects placed near its surface. A person standing on the surface of the earth will.
A force F1 acts on a particle accelerating it from rest to a velocity v. Force F1 is then replaced by F2 which decelerates the particle to rest.
In an imaginary atmosphere, the air exerts a small force F on any particle in the direction of the particle's motion. A particle of mass m projected upward takes time t1 in reaching the maximum height and t2 in the return journey to the original point. Then.
A particle stays at rest as seen in a frame. We can conclude that
(a) the frame is inertial
(b) resultant force on the particle is zero
(c) the frame may be inertial but the resultant force on the particle is zero
(d) the frame may be non-inertial but there is a non-zero resultant force
A particle is found to be at rest when seen from a frame S1 and moving with constant velocity when seen from another frame S2. Mark out the possible options.
(a) Both the frames are inertial.
(b) Both the frames are non-inertial.
(c) S1 is inertial and S2 is non-inertial.
(d) S1 is non-inertial and S2 is inertial
State and explain the law of inertia (or Newton's first law of motion).
How does Newton's second law of motion differ from the first law of motion?
Give two examples of the following:
Inertia of rest
If a 5 N and a 15 N forces are acting opposite to one another. Find the resultant force and the direction of action of the resultant force.
When a bus suddenly takes a tum, the passengers are thrown outwards because of
A smooth sphere of radius R and mass M is placed on the smooth horizontal floor. Another smooth particle of mass m is placed on the sphere and a horizontal force F is applied on the sphere as shown. If the particle does not slip on the sphere then the value of force F is ______.

This question has Statement 1 and Statement 2. Of the four choices given after the Statements, choose the one that best describes the two Statements.
Statement 1: If you push on a cart being pulled by a horse so that it does not move, the cart pushes you back with an equal and opposite force.
Statement 2: The cart does not move because the force described in statement 1 cancel each other.
Match the following.
| Column I | Column II |
| a. Newton’s I law | propulsion of a rocket |
| b. Newton’s II law | Stable equilibrium of the body |
| c. Newton’s III law | Law of force |
| d. Law of conservation of Linear momentum | Flying nature of bird |
