Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In an imaginary atmosphere, the air exerts a small force F on any particle in the direction of the particle's motion. A particle of mass m projected upward takes time t1 in reaching the maximum height and t2 in the return journey to the original point. Then.
Options
t1 < t2
t1 > t2
t1 = t2
the relation between t1 and t2 depends on the mass of the particle
Solution
t1 > t2
Let acceleration due to air resistance force be a.
Let H be maximum height attained by the particle.
Direction of air resistance force is in the direction of motion.
In the upward direction of motion,
\[a_{eff} = \left| g - a \right|\]
\[t_1 = \sqrt{\frac{2H}{\left| g - a \right|}} . . . (1)\]
In the downward direction of motion,
\[a_{eff} = g + a\]
\[t_2 = \sqrt{\frac{2H}{g + a}} . . . (2)\]
So, t1 > t2.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on a drop of rain falling down with a constant speed.
Name the physical quantity whose unit is ‘newton’.
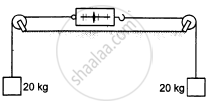
The figure shows a light spring balance connected to two blocks of mass 20 kg each. The graduations in the balance measure the tension in the spring. (a) What is the reading of the balance? (b) Will the reading change if the balance is heavy, say 2.0 kg? (c) What will happen if the spring is light but the blocks have unequal masses?
The acceleration of a particle is zero, as measured from an inertial frame of reference. Can we conclude that no force acts on the particle?
The force exerted by the floor of an elevator on the foot of a person is more than the weight of the person if the elevator is
(a) going up and slowing down
(b) going up and speeding up
(c) going down and slowing down
(d) going down and speeding up
A block of mass 2 kg placed on a long frictionless horizontal table is pulled horizontally by a constant force F. It is found to move 10 m in the first seconds. Find the magnitude of F.
If you jump barefoot on a hard surface, your legs are injured. But they are not injured if you jump on a soft surface like sand or pillow. Why?
When a train starts, the head of a standing passenger seems to be pushed backward. Analyse the situation from the ground frame. Does it really go backward? Coming back to the train frame, how do you explain the backward movement of the head on the basis of Newton's laws?
Give qualitative definition of force on the basic of Newton's first law of motion.
Give one example each of inertia of rest and inertia of motion.
Give two examples of the following:
Inertia of motion
Match the following
| Column I | Column II |
| Newton’s I law | propulsion of a rocket |
| Newton’s II law | Stable equilibrium of a body |
| Newton’s III law | Law of force |
| Law of conservation of linear momentum | Flying nature of bird |
Classify the types of force based on their application.
A body of mass 10 kg is acted upon by two perpendicular forces, 6 N and 8 N. The resultant acceleration of the body is ______.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
A mass of 2 kg is suspended with thread AB (Figure). Thread CD of the same type is attached to the other end of 2 kg mass. Lower thread is pulled gradually, harder and harder in the downward directon so as to apply force on AB. Which of the threads will break and why?

In the above given problem if the lower thread is pulled with a jerk, what happens?
Block A of weight 100 N rests on a frictionless inclined plane of slope angle 30° (figure). A flexible cord attached to A passes over a frictonless pulley and is connected to block B of weight W. Find the weight W for which the system is in equilibrium.

A force F is applied to the initially stationary cart. The variation of force with time is shown in the figure. The speed of the cart at t = 5 sec is ______.

Match the following.
| Column I | Column II |
| a. Newton’s I law | propulsion of a rocket |
| b. Newton’s II law | Stable equilibrium of the body |
| c. Newton’s III law | Law of force |
| d. Law of conservation of Linear momentum | Flying nature of bird |
