Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A smooth wedge A is fitted in a chamber hanging from a fixed ceiling near the earth's surface. A block B placed at the top of the wedge takes time T to slide down the length of the wedge. If the block is placed at the top of the wedge and the cable supporting the chamber is broken at the same instant, the block will.
Options
take a time longer than T to slide down the wedge
take a time shorter than T to slide down the wedge
remain at the top of the wedge
jump off the wedge
Solution
remain at the top of the wedge
Downward gravitational force will be balanced by the upward pseudo force (because of the motion of the wedge in downward direction). The block will remain at its position, as both the box and the inclined plane are falling with the same acceleration (g).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A constant retarding force of 50 N is applied to a body of mass 20 kg moving initially with a speed of 15 ms–1. How long does the body take to stop?
Two masses 8 kg and 12 kg are connected at the two ends of a light, inextensible string that goes over a frictionless pulley. Find the acceleration of the masses, and the tension in the string when the masses are released.
When a horse pulls a cart, the force that helps the horse to move forward is the force exerted by
In a TV picture tube, electrons are ejected from the cathode with negligible speed and they attain a velocity of 5 × 106 m/s in travelling one centimetre. Assuming straight-line motion, find the constant force exerted on the electrons. The mass of an electron is 9.1 × 10−31 kg.
Two blocks of equal mass m are tied to each other through a light string. One of the blocks is pulled along the line joining them with a constant force F. Find the tension in the string joining the blocks.
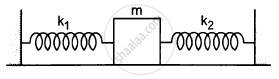
Both the springs shown in the following figure are unstretched. If the block is displaced by a distance x and released, what will be the initial acceleration?
A person is standing on a weighing machine placed on the floor of an elevator. The elevator starts going up with some acceleration, moves with uniform velocity for a while and finally decelerates to stop. The maximum and the minimum weights recorded are 72 kg and 60 kg, respectively. Assuming that the magnitudes of acceleration and deceleration are the same, find (a) the true weight of the person and (b) the magnitude of the acceleration. Take g = 9.9 m/s2.
An empty plastic box of mass m is found to accelerate up at the rate of g/6 when placed deep inside water. How much sand should be put inside the box so that it may accelerate down at the rate of g/6?
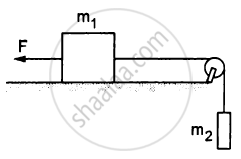
A constant force F = m2g/2 is applied on the block of mass m1 as shown in the following figure. The string and the pulley are light and the surface of the table is smooth. Find the acceleration of m1.
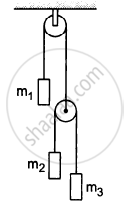
Let m1 = 1 kg, m2 = 2 kg and m3 = 3 kg in the following figure. Find the accelerations of m1, m2 and m3. The string from the upper pulley to m1 is 20 cm when the system is released from rest. How long will it take before m1 strikes the pulley?
Find the acceleration of the 500 g block in the following figure.
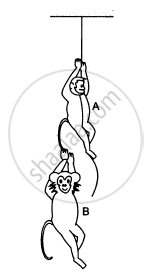
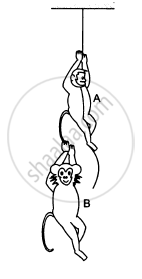
The monkey B, shown in the following figure, is holding on to the tail of monkey A that is climbing up a rope. The masses of monkeys A and B are 5 kg and 2 kg, respectively. If A can tolerate a tension of 30 N in its tail, what force should it apply on the rope in order to carry monkey B with it? Take g = 10 m/s2.
An aeroplane is moving uniformly at a constant height under the action of two forces (i) Upward force (lift) and (ii) Downward force (weight). What is the net force on the aeroplane?
Calculate the magnitude of force which when applied on a body of mass 0.5 kg produces an acceleration of 5 m s-2.
A force acts for 10 s on a stationary body of mass 100 kg, after which the force ceases to act. The body moves through a distance of 100 m in the next 5 s. Calculate : The magnitude of the force
How long will a stone take to fall to the ground from the top of a building 80 m high
An electron of mass 9 × 10−31 kg is moving with a linear velocity of 6 × 107 ms−1. Calculate the linear momentum of electron.
Define Newton’s second law of motion.
A stone is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 9.8 m/s. When will it reach the ground?
A stone is dropped from a tower 98 m high. With what speed should a second stone be thrown 1 s later so that both hit the ground at the same time?
