Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A smooth wedge A is fitted in a chamber hanging from a fixed ceiling near the earth's surface. A block B placed at the top of the wedge takes time T to slide down the length of the wedge. If the block is placed at the top of the wedge and the cable supporting the chamber is broken at the same instant, the block will.
विकल्प
take a time longer than T to slide down the wedge
take a time shorter than T to slide down the wedge
remain at the top of the wedge
jump off the wedge
उत्तर
remain at the top of the wedge
Downward gravitational force will be balanced by the upward pseudo force (because of the motion of the wedge in downward direction). The block will remain at its position, as both the box and the inclined plane are falling with the same acceleration (g).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A person says that he measured the acceleration of a particle to be non-zero even though no force was acting on the particle.
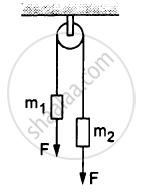
A constant force F = m2g/2 is applied on the block of mass m1 as shown in the following figure. The string and the pulley are light and the surface of the table is smooth. Find the acceleration of m1.
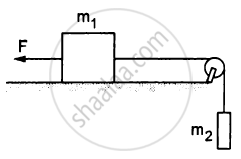
In the following figure, m1 = 5 kg, m2 = 2 kg and F = 1 N. Find the acceleration of either block. Describe the motion of m1 if the string breaks but F continues to act.
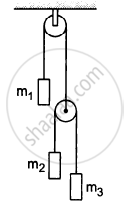
Let m1 = 1 kg, m2 = 2 kg and m3 = 3 kg in the following figure. Find the accelerations of m1, m2 and m3. The string from the upper pulley to m1 is 20 cm when the system is released from rest. How long will it take before m1 strikes the pulley?
In the previous problem, suppose m2 = 2.0 kg and m3 = 3.0 kg. What should be the mass m, so that it remains at rest?
Show that the rate of change of momentum = mass × acceleration. Under what condition does this relation hold?
State the Newton's second law of motion. What information do you get from it?
State Newton's second law of motion. Under what condition does it take the form F = ma?
The linear momentum of a ball of mass 50 g is 0.5 kg m s-1. Find its velocity.
A force of 10 N acts on a body of mass 2 kg for 3 s, initially at rest. Calculate : The velocity acquired by the body
A bullet of mass 50 g moving with an initial velocity 100 m s-1 strikes a wooden block and comes to rest after penetrating a distance 2 cm in it. Calculate: (i) Initial momentum of the bullet, (ii) Final momentum of the bullet, (iii) Retardation caused by the wooden block and (iv) Resistive force exerted by the wooden block.
How long will a stone take to fall to the ground from the top of a building 80 m high
What causes motion in a body?
Why is it advantageous to turn before taking a long jump?
What do you mean by an impulsive force?
Use Newton's second law to explain the following:
We always prefer to land on sand instead of hard floor while taking a high jump.
A stone is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 9.8 m/s. When will it reach the ground?
A cricket ball of mass 150 g has an initial velocity `u = (3hati + 4hatj)` m s−1 and a final velocity `v = - (3hati + 4hatj)` m s−1 after being hit. The change in momentum (final momentum-initial momentum) is (in kg m s1)
Figure shows (x, t), (y, t ) diagram of a particle moving in 2-dimensions.
|
|
 (b) |
If the particle has a mass of 500 g, find the force (direction and magnitude) acting on the particle.

