Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The linear momentum of a ball of mass 50 g is 0.5 kg m s-1. Find its velocity.
उत्तर
Linear momentum = 0.5 kg m/s
Mass, m = 50 g = 0.05 kg
Velocity = Linear momentum/mass
= 0.5/0.05 m/s
= 10 m/s -1
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A man has fallen into a ditch of width d and two of his friends are slowly pulling him out using a light rope and two fixed pulleys as shown in the following figure. Show that the force (assumed equal for both the friends) exerted by each friend on the road increases as the man moves up. Find the force when the man is at a depth h.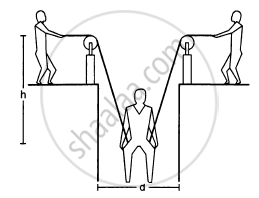
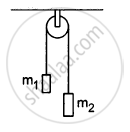
In a simple Atwood machine, two unequal masses m1 and m2 are connected by a string going over a clamped light smooth pulley. In a typical arrangement (In the following figure), m1 = 300 g and m2 = 600 g. The system is released from rest. (a) Find the distance travelled by the first block in the first two seconds; (b) find the tension in the string; (c) find the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley.
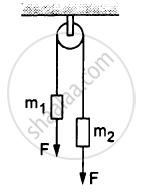
In the following figure, m1 = 5 kg, m2 = 2 kg and F = 1 N. Find the acceleration of either block. Describe the motion of m1 if the string breaks but F continues to act.
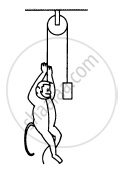
A monkey is climbing on a rope that goes over a smooth light pulley and supports a block of equal mass at the other end in the following figure. Show that whatever force the monkey exerts on the rope, the monkey and the block move in the same direction with equal acceleration. If initially both were at rest, their separation will not change as time passes.
An aeroplane is moving uniformly at a constant height under the action of two forces (i) Upward force (lift) and (ii) Downward force (weight). What is the net force on the aeroplane?
Two bodies A and B of same mass are moving with velocities v and 2v, respectively. Compare their (i) inertia and (ii) momentum.
The linear momentum of a body of mass m moving with velocity v is :
An electron of mass 9 × 10−31 kg is moving with a linear velocity of 6 × 107 ms−1. Calculate the linear momentum of electron.
Prove mathematically F = ma
Use Newton's second law to explain the following:
While catching a fast moving ball, we always pull our hands backwards.
