Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
![Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 3 - Laws of Motion Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 3 - Laws of Motion - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-physics-english-class-9-icse_6:8a0c4572dea049a29e575abe2d9ca662.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 3: Laws of Motion
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 3 of CISCE Selina for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 3 Laws of Motion Exercise 3 (A) [Pages 59 - 60]
Explain giving two examples of following :
Contact forces
Explain giving two examples of following :
Non - contact forces
Classify the following amongst contact and non - contact forces:
Frictional force
Normal reaction force
Force of tension in a string
Gravitational force
Electrostatic force
Magnetic force
Give one example in each case where :
The force is of contact, and
Force is at a distance
A ball is hanging by string from the ceiling of the roof. Draw a neat labelled diagram showing the forces acting on the ball and the string.
A spring is compressed against a rigid wall. Draw a neat and labeled diagram showing the forces acting on the spring.
A wooden block is placed on a table top. Name the forces acting on the block and draw a neat and labelled diagram to show the point of application and direction of these forces.
State one factor on which the magnitude of a non-contact force depends. How does it depend on the factor stated by you?
The separation between two masses is reduced to half. How is the magnitude of gravitational force between them affected?
State the effects of a force applied on
- A non-rigid, and
- A rigid body.
How does the effect of the force differ in the two cases?
Give one example in each of the following cases where a force:
(i) Stops a moving body.
(ii) Moves a stationary body.
(iii) Changes the size of a body.
(iv) Changes the shape of a body.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 3 Laws of Motion Exercise 3 (A) [Page 60]
Which of the following is a contact force:
Electrostatic force
Gravitational force
Frictional force
Magnetic force
The non - contact force is :
Force of reaction
Force due to gravity
Tension in string
Force of friction
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 3 Laws of Motion Exercise 3 (B) [Page 63]
Name the physical quantity that causes motion in a body.
Is force needed to keep a moving body in motion?
A ball moving on a table top eventually stops. Explain the reason .
A ball is moving on a perfectly smooth horizontal surface. If no force is applied on it, then will its speed decrease, increase or remain unchanged?
What is Galileo's law of inertia?
State Newton's first law of motion.
State and explain the law of inertia (or Newton's first law of motion).
What is meant by the term inertia?
Give qualitative definition of force on the basic of Newton's first law of motion.
Name the factor on which the inertia of a body depends and state how does it depend on the factor stated by you .
Give two examples to show that greater the mass, greater is the inertia of the body.
'More the mass, the more difficult it is to move the body from rest'. Explain this statement by giving an example.
Name the two kinds of inertia.
Give one example of each of the following :
(a) inertia of rest, and (b) inertia of motion .
Two equal and opposite forces act on a stationary body. Will the body move? Give a reason to your answer.
Two equal and opposite forces act on a moving object. How is its motion affected? Give reason.
An aeroplane is moving uniformly at a constant height under the action of two forces (i) Upward force (lift) and (ii) Downward force (weight). What is the net force on the aeroplane?
Why does a person fall when he jumps out from a moving train ?
Why does a coin, placed on a card, drop into the tumbler when the card is rapidly flicked with a finger?
Why does a ball thrown vertically upwards in a moving train , come back to the thrower's hand ?
Explain the following :
When a train suddenly moves forward , the passenger standing in the compartment tends to fall backwards .
Explain the following :
When a corridor train suddenly starts , the sliding doors of some compartments may open .
Explain the following:
People often shake the branches of a tree for getting down its fruits.
Explain the following :
After alighting from a moving bus , one has to run for some distance in the direction of bus in order to avoid falling .
Dust particles are removed from a carpet by beating it.
Explain the following :
It is advantageous to run before taking a long jump .
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 3 Laws of Motion Exercise 3 (B) [Page 64]
The property of inertia is more in :
a car
a truck
a horse cart
a toy car
A tennis ball and a cricket ball , both are stationary. To start motion in them .
a less force is required for the cricket ball than for the tennis ball .
a less force is required for the tennis ball than for the cricket ball
same force is required for both the balls .
nothing can be said .
A force is needed to :
Change the state of motion or state of rest of the body .
Keep the body in motion
keep the body stationary
keep the velocity of body constant .
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 3 Laws of Motion Exercise 3 (C) [Page 69]
Name the two factors on which the force needed to stop a moving body in a given time depends.
Define linear momentum and state its S.I. unit.
A body of mass m moving with a velocity v is acted upon by a force. Write an expression for change in momentum in each of the following cases: (i) When v << c, (ii) When v → c and (iii) When v << c but m does not remain constant. Here, c is the speed of light.
Show that the rate of change of momentum = mass × acceleration. Under what condition does this relation hold?
Two bodies A and B of same mass are moving with velocities v and 2v, respectively. Compare their (i) inertia and (ii) momentum.
Two balls A and B of masses m and 2 m are in motion with velocities 2v and v, respectively. Compare:
(i) Their inertia.
(ii) Their momentum.
(iii) The force needed to stop them in the same time.
State the Newton's second law of motion. What information do you get from it?
How does Newton's second law of motion differ from the first law of motion?
Write the mathematical form of Newton's second law of motion. State the conditions if any.
State Newton's second law of motion. Under what condition does it take the form F = ma?
How can Newton's first law of motion be obtained from the second law of motion?
Draw a graph to show the dependence of acceleration on force for a constant mass.
Draw a graph to show the dependence of force on mass for a constant acceleration.
How does the acceleration produced by a given force depend on the mass of the body? Draw a graph to show it.
Name the S.I. unit of force and define it .
What is the C.G.S. unit of force? How is it defined?
Name the S.I. and C.G.S. units of force. How are they related?
Why does a glass vessel break when it falls on a hard floor, but it does not break when it falls on a carpet?
Use Newton's second law of motion to explain the following instance :
A cricketer pulls his hands back while catching a fast moving cricket ball .
Use Newton's second law of motion to explain the following instance :
An athlete prefers to land on sand instead of hard floor while taking a high jump .
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 3 Laws of Motion Exercise 3 (C) [Page 70]
The linear momentum of a body of mass m moving with velocity v is :
v/m
m/v
mv
1/mv
The unit of linear momentum is :
N s
kg m s-2
N s-1
kg2 m s-1
The correct form of Newton's second law is :
F = `(Δ"p")/(Δ"t")`
`"F"= "m"(Δ"v")/(Δ"t")`
`"F = v"(Δ"m")/(Δ"t")"`
F = mv
The acceleration produced in a body by a force of given magnitude depends on
size of the body
shape of the body
mass of the body
none of these
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 3 Laws of Motion Exercise 3 (C) [Page 70]
A body of mass 5 kg is moving with velocity 2 m s-1. Calculate its linear momentum.
The linear momentum of a ball of mass 50 g is 0.5 kg m s-1. Find its velocity.
A force of 15 N acts on a body of mass 2 kg. Calculate the acceleration produced.
A force of 10 N acts on a body of mass 5 kg. Find the acceleration produced.
Calculate the magnitude of force which when applied on a body of mass 0.5 kg produces an acceleration of 5 m s-2.
A force of 10 N acts on a body of mass 2 kg for 3 s, initially at rest. Calculate : The velocity acquired by the body
A force of 10 N acts on a body of mass 2 kg for 3 s, initially at rest. Calculate : Change in momentum of the body.
A force acts for 10 s on a stationary body of mass 100 kg, after which the force ceases to act. The body moves through a distance of 100 m in the next 5 s. Calculate: The velocity acquired by the body.
A force acts for 10 s on a stationary body of mass 100 kg, after which the force ceases to act. The body moves through a distance of 100 m in the next 5 s. Calculate : The acceleration produced by the force
A force acts for 10 s on a stationary body of mass 100 kg, after which the force ceases to act. The body moves through a distance of 100 m in the next 5 s. Calculate : The magnitude of the force
Figure shows the velocity-time graph of a particle of mass 100 g moving in a straight line. Calculate the force acting on the particle.
(Hint : Acceleration = Slope of the v-t graph)

A force causes an acceleration of 10 m s-2 in a body of mass 500 g. What acceleration will be caused by the same force in a body of mass 5 kg?
A force acts for 0.1 s on a body of mass 2.0 kg initially at rest. The force is then withdrawn and the body moves with a velocity of 2 m s-1. Find the magnitude of the force.
A body of mass 500 g, initially at rest, is acted upon by a force which causes it to move a distance of 4 m in 2 s, Calculate the force applied.
A car of mass 480 kg moving at a speed of 54 km h-1 is stopped by applying brakes in 10 s . Calculate the force applied by the brakes .
A car is moving with a uniform velocity 30 ms-1. It is stopped in 2 s by applying a force of 1500 N through its brakes. Calculate the following values : The change in momentum of car.
A car is moving with a uniform velocity 30 ms-1. It is stopped in 2 s by applying a force of 1500 N through its brakes. Calculate the following values : The retardation produced in car.
A car is moving with a uniform velocity of 30 ms-1. It is stopped in 2 s by applying a force of 1500 N through its brakes. Calculate: The mass of car.
A bullet of mass 50 g moving with an initial velocity 100 m s-1 strikes a wooden block and comes to rest after penetrating a distance 2 cm in it. Calculate: (i) Initial momentum of the bullet, (ii) Final momentum of the bullet, (iii) Retardation caused by the wooden block and (iv) Resistive force exerted by the wooden block.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 3 Laws of Motion Exercise 3 (D) [Page 73]
State the usefulness of Newton's third law of motion .
State Newton's third law of motion.
State and explain the law of action and reaction. by giving two examples.
Name and state the action and reaction in the following case :
Firing a bullet from a gun
Name and state the action and reaction in the following case :
Hammering a nail
Name and state the action and reaction in the following case :
A book lying on a table
Name and state the action and reaction in the following case :
A moving rocket
Name and state the action and reaction in the following case :
A person moving on the floor
Name and state the action and reaction in the following case :
A moving train colliding with a stationary train
Explain the motion of a rocket with the help of Newton's third law.
When a shot is fired from a gun, the gun is recoiled. Explain.
When you step ashore from a stationary boat, it tends to leave the shore. Explain.
When two spring balances joined at their free ends are pulled apart, both show the same reading. Explain.
To move a boat ahead in water, the boatman has to push the water backwards by his oar. Explain this statement.
A person pushing a wall hard is liable to fall back. Give reason.
The action and reaction both act simultaneously. Is this statement true?
The 'Action and reaction are equal in magnitude'. Is this statement true?
A light ball falling on ground, after striking the ground rises upwards. Explain the reason.
Comment on the statement 'the sum of action and reaction on a body is zero'.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 3 Laws of Motion Exercise 3 (D) [Page 73]
Newton's third law :
defines the force qualitatively
Defines the force quantitatively.
Explains the way the force acts on a body .
Gives the direction of force.
Action and reaction act on :
Same body in opposite directions.
Different bodies in oppposite directions.
Different bodies , but in the same direction.
Same body in the same direction.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 3 Laws of Motion Exercise 3 (D) [Page 73]
A boy pushes a wall with a force of 10 N towards east. What force is exerted by the wall on the boy?
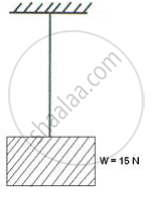
In the Figure a block of weight 15 N is hanging from a rigid support by a string. What force is exerted by (a) a block on the string and (b) a string on the block? Name and show them in the diagram.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 3 Laws of Motion Exercise 3 (E) [Pages 79 - 80]
Write the answer of the question with reference to laws of gravitation.
State the universal law of gravitation.
State whether the gravitational force between two masses is attractive or repulsive ?
Write an expression for the gravitational force of attraction between two bodies of masses m1 and m2 separated by a distance r.
How does the gravitational force of attraction between two masses depend on the distance between them?
How is the gravitational force between two masses affected if the separation between them is doubled?
Define gravitational constant G.
Write the numerical value of gravitational constant G with its S.I. unit .
What is the importance of law of gravitation ?
What do you understand by the term force due to gravity ?
Write an expression for the force due to gravity on a body of mass m and explain the meaning of symbols used in it.
Define the term acceleration due to gravity? Write its S.I. unit.
Write down the average value of g on Earth's surface ?
How is the acccelaration due to gravity on the surface of the earth realted to its mass and radius ?
How are g and G realated ?
A body falls freely under gravity from rest and reaches the ground in time t. Write the expression for the height fallen by the body.
A body is thrown vertically upwards with an initial velocity u. Write the expression for the maximum height attained by the body.
Define the terms mass and weight.
Distinguish between mass and weight.
State the S.I. units of (a) mass and (b) weight.
The value of g at the centre of Earth is zero. What will be the weight of a body of mass m kg at the centre of the Earth?
Which of the following quantity does not change by change of place of a body : mass or weight ?
Explain the meaning of the following statement '1 kgf = 9.8 N'.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 3 Laws of Motion Exercise 3 (E) [Page 80]
The gravitational force between two bodies is :
Always repulsive
always attractive
attractive only at large distance
Repulsive only at large distance .
The value of G is :
9.8 N m2 kg-2
6.7 x 10-11 N m2 kg-2
6.7 x 10-11 m s-2
6.7 N kg-1
The force of attraction between two masses each of 1 kg kept at a separation of 1 m is :
9.8 N
6.7 N
980 N
6.7 × 10-11 N
A body is projected vertically upward with an initial velocity u . If acceleartion due to gravity is g , the time for which it remains in air , is :
`u/g`
ug
`(2u)/g`
`u/(2g)`
An object falling freely from rest reaches ground in 2 s. If acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m s-2, then the velocity of object on reaching the ground will be
9.8 m s-1
4.9 m s-1
19.6 m s-1
Zero
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE 3 Laws of Motion Exercise 3 (E) [Pages 80 - 81]
The force of attraction between two bodies at certain separation is 10 N. What will be the force of attraction between them if the separation is reduced to half?
Write the approximate weight of a body of mass 5 kg. What assumption have you made?
Calculate the weight of a body of mass 10 kg in (a) kgf and (b) newton. Take g = 9.8 m s-2.
State the magnitude and direction of the force of gravity acting on the body of mass 5 kg. Take g = 9.8 m s-2.
The weight of a body is 2.0 N. What is the mass of the body? (g = 10 m s-2)
The weight of a body on Earth is 98 N, where acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m s-2. What will be its (a) mass and (b) weight on the Moon, where acceleration due to gravity is 1.6 m s-2?
A man weighs 600 N on the Earth. What would be his approximate weight on the Moon? Give a reason for your answer?
What is the (a) force of gravity and (b) weight of a block of mass 10.5 kg ? Take g = 10 ms-2 .
A ball is released from a height and it reaches the ground in 3 s. If g= 9.8 m s-2 Find :
the height from which the ball was released
A ball is released from a height and it reaches the ground in 3 s. If g= 9.8 m s-2 Find :
the velocity with which the ball will strike the ground .
What force, in newton, your muscles need to apply to hold a mass of 5 kg in your hand? State the assumption.
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. It goes to a height 20 m and then returns to the ground. Taking acceleration due to gravity g to be 10 ms-2, find: the initial velocity of the ball.
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. It goes to a height 20 m and then returns to the ground. Taking acceleration due to gravity g to be 10 ms-2 , find :
the final velocity of the ball on reaching the ground .
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. It goes to a height 20 m and then returns to the ground. Taking acceleration due to gravity g to be 10 ms-2 , find :
the total time of journey of the ball .
An body is dropped from the top of a tower. It acquires a velocity 20 m s-1 on reaching the ground. Calculate the height of the tower. (Take g = 10 m s-2)
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. It returns 6 s later. Calculate : The greatest height reached by the ball . (Take g = 10 m s-2)
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. It returns 6 s later. Calculate : the initial velocity of the ball (Take g = 10 m s-2)
A pebble is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 20 m s-1. How high will it be after 2 s? (Take g = 10 m s-2)
How long will a stone take to fall to the ground from the top of a building 80 m high
What will be the velocity of the stone on reaching the ground? (Take g=10 m s-2)
A body falls from the top of a building and reaches the ground 2.5 s later. How high is the building? (Take g = 9.8 m s-2)
A ball is thrown vertically upwards with an initial velocity of 49 m s-1 . calculate : the maximum height attained .
ball is thrown vertically upwards with an initial velocity of 49 m s-1. Calculate: The time taken by it before it reaches the ground again. (Take g = 9.8 m s-2).
A stone is dropped freely from the top of a tower and it reaches the ground in 4 s. Taking g = 10m s-2, calculate the height of the tower.
A pebble is dropped freely in a well from its top. It takes 20 s for the pebble to reach the water surface in the well. Taking g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 330 m s-1. Find : The depth of water surface
A pebble is dropped freely in a well from its top. It takes 20 s for the pebble to reach the water surface in the well. Taking g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 330 m s-1. Find : The time when echo is heard after the pebble is dropped.
A ball is thrown vertically upwards from the top of a tower with an initial velocity of 19.6 m s-1. The ball reaches the ground after 5 s. Calculate: (i) The height of the tower, (ii) The velocity of the ball on reaching the ground. Take g= 9.8 ms-2.
Solutions for 3: Laws of Motion
![Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 3 - Laws of Motion Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 3 - Laws of Motion - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-physics-english-class-9-icse_6:8a0c4572dea049a29e575abe2d9ca662.jpg)
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 3 - Laws of Motion
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE 3 (Laws of Motion) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 3 Laws of Motion are Newton's First Law of Motion, Newton’s Second Law of Motion, Free Fall, Gravitational Units of Force, Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation, Newton's Third Law of Motion, Newton’s Second Law of Motion in Terms of Rate of Change of Momentum, Force Due to Gravity, Acceleration Due to Gravity (Earth’s Gravitational Acceleration), Concept of Mass and Weight, Effect of Force, Types of Force: Contact Force, Types of Force: Non-Contact Force, Inertia and Mass, Types of Inertia, Linear Momentum, Change in Momentum, Rate of Change of Momentum.
Using Selina Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE solutions Laws of Motion exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 3, Laws of Motion Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Concise Physics [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
