Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Give one example in each of the following cases where a force:
(i) Stops a moving body.
(ii) Moves a stationary body.
(iii) Changes the size of a body.
(iv) Changes the shape of a body.
उत्तर
- A fielder on the ground stops a moving ball by applying a force with his hands.
- The pull exerted by horse makes a cart moves.
- In a cycle pump, when the piston is lowered, the air is compressed to occupy a less volume.
- On pressing a piece of rubber, its shape changes.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A ball is hanging by string from the ceiling of the roof. Draw a neat labelled diagram showing the forces acting on the ball and the string.
A wooden block is placed on a table top. Name the forces acting on the block and draw a neat and labelled diagram to show the point of application and direction of these forces.
State the effects of a force applied on
- A non-rigid, and
- A rigid body.
How does the effect of the force differ in the two cases?
Is force needed to keep a moving body in motion?
Two equal and opposite forces act on a moving object. How is its motion affected? Give reason.
A cricket player holds a cricket ball of mass 100 g by moving his hands backward by 0.75 m. If the initial velocity of the ball is 108 kmh−1, find the retarding force applied by the player.
Explain the following:
Why do we jerk wet clothes before spreading them on a line?
What is a force?
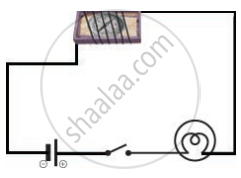
In the circuit shown in figure, when the key is closed, the compass needle placed in the match box deflects. Name the force which cases this deflection.
During dry weather, clothes made of synthetic fibre often stick to the skin. Which type of force is responsible for this phenomenon?
