Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State the magnitude and direction of the force of gravity acting on the body of mass 5 kg. Take g = 9.8 m s-2.
उत्तर
Mass = 5 kg.
g = 9.8 m/s2.
Let F be the force of gravity,
F = mg.
F = (5) (9.8) = 49 N.
Force of gravity always acts downwards.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A force \[\vec{F} = \vec{v} \times \vec{A}\] is exerted on a particle in addition to the force of gravity, where \[\vec{v}\] is the velocity of the particle and \[\vec{A}\] is a constant vector in the horizontal direction. With what minimum speed, a particle of mass m be projected so that it continues to move without being defelected and with a constant velocity?
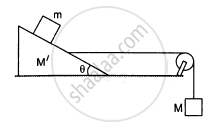
Find the mass M of the hanging block in the following figure that will prevent the smaller block from slipping over the triangular block. All the surfaces are frictionless and the strings and the pulleys are light.
A tennis ball and a cricket ball , both are stationary. To start motion in them .
How can Newton's first law of motion be obtained from the second law of motion?
Use Newton's second law of motion to explain the following instance :
A cricketer pulls his hands back while catching a fast moving cricket ball .
Use Newton's second law of motion to explain the following instance :
An athlete prefers to land on sand instead of hard floor while taking a high jump .
A body of mass 5 kg is moving with velocity 2 m s-1. Calculate its linear momentum.
Define Newton’s second law of motion.
Prove mathematically F = ma
What do you mean by an impulsive force?
