Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How can Newton's first law of motion be obtained from the second law of motion?
उत्तर
From Newton's second law of motion, F = ma.
If F = 0, then a = 0.
This means that if no force is applied on the body, its acceleration will be zero. If the body is at rest, then it will remain in the state of rest and if it is moving, then it will remain moving in the same direction with the same speed. Thus, a body not acted upon by an external force, does not change its state of rest or motion. This is the statement of Newton's first law of motion.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain why a cricketer moves his hands backwards while holding a catch.
In a TV picture tube, electrons are ejected from the cathode with negligible speed and they attain a velocity of 5 × 106 m/s in travelling one centimetre. Assuming straight-line motion, find the constant force exerted on the electrons. The mass of an electron is 9.1 × 10−31 kg.
A particle of mass 0.3 kg is subjected to a force F = −kx with k = 15 N/m. What will be its initial acceleration if it is released from a point x = 20 cm?
A small block B is placed on another block A of mass 5 kg and length 20 cm. Initially, the block B is near the right end of block A (In the following Figure). A constant horizontal force of 10 N is applied to the block A. All the surfaces are assumed frictionless. Find the time that elapses before block B separates from A.

A force \[\vec{F} = \vec{v} \times \vec{A}\] is exerted on a particle in addition to the force of gravity, where \[\vec{v}\] is the velocity of the particle and \[\vec{A}\] is a constant vector in the horizontal direction. With what minimum speed, a particle of mass m be projected so that it continues to move without being defelected and with a constant velocity?
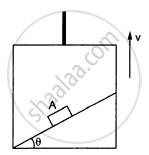
A block A can slide on a frictionless incline of angle θ and length l, kept inside an elevator going up with uniform velocity v in the following figure. Find the time taken by the block to slide down the length of the incline if it is released from the top of the incline.
Use Newton's second law of motion to explain the following instance :
A cricketer pulls his hands back while catching a fast moving cricket ball .
A force of 10 N acts on a body of mass 2 kg for 3 s, initially at rest. Calculate : Change in momentum of the body.
ame the law of motion which gives the definition of force.
What do you mean by linear momentum of a body? A force causes an acceleration of 10 ms-2 in a body of mass 1 kg. What acceleration will be caused by the same force in a body of mass 4 kg?
