Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A force \[\vec{F} = \vec{v} \times \vec{A}\] is exerted on a particle in addition to the force of gravity, where \[\vec{v}\] is the velocity of the particle and \[\vec{A}\] is a constant vector in the horizontal direction. With what minimum speed, a particle of mass m be projected so that it continues to move without being defelected and with a constant velocity?
उत्तर
For the particle to move without being deflected and with constant velocity, the net force on the particle should be zero.
\[\vec{F} + m \vec{g} = 0\]
\[\Rightarrow \left( \vec{v} \times \vec{A} \right) + \vec{mg} = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( \vec{v} \times \vec{A} \right) = - \vec{mg}\]
\[\left| vA\sin\theta \right| = \left| mg \right|\]
\[\therefore v = \frac{mg}{A\sin\theta}\]
v will be minimum when sinθ = 1.
⇒ θ = 90°
\[\therefore v_{\text{min}} = \frac{mg}{A}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A batsman deflects a ball by an angle of 45° without changing its initial speed which is equal to 54 km/h. What is the impulse imparted to the ball? (Mass of the ball is 0.15 kg.)
Explain why a cricketer moves his hands backwards while holding a catch.
The rear side of a truck is open and a box of 40 kg mass is placed 5 m away from the open end as shown in Figure. The coefficient of friction between the box and the surface below it is 0.15. On a straight road, the truck starts from rest and accelerates with 2 m s–2. At what distance from the starting point does the box fall off the truck? (Ignore the size of the box).

A small block B is placed on another block A of mass 5 kg and length 20 cm. Initially, the block B is near the right end of block A (In the following Figure). A constant horizontal force of 10 N is applied to the block A. All the surfaces are assumed frictionless. Find the time that elapses before block B separates from A.

Find the reading of the spring balance shown in the following figure. The elevator is going up with an acceleration g/10, the pulley and the string are light and the pulley is smooth.

In a simple Atwood machine, two unequal masses m1 and m2 are connected by a string going over a clamped light smooth pulley. In a typical arrangement (In the following figure), m1 = 300 g and m2 = 600 g. The system is released from rest. (a) Find the distance travelled by the first block in the first two seconds; (b) find the tension in the string; (c) find the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley.
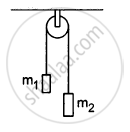
In the following figure, m1 = 5 kg, m2 = 2 kg and F = 1 N. Find the acceleration of either block. Describe the motion of m1 if the string breaks but F continues to act.
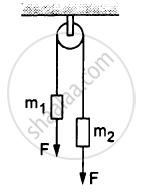
Consider the situation shown in the following figure. Both the pulleys and the string are light and all the surfaces are frictionless. (a) Find the acceleration of the mass M; (b) find the tension in the string; (c) calculate the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley A in the figure.
State the Newton's second law of motion. What information do you get from it?
The correct form of Newton's second law is :
The unit of linear momentum is :
A bullet of mass 50 g moving with an initial velocity 100 m s-1 strikes a wooden block and comes to rest after penetrating a distance 2 cm in it. Calculate: (i) Initial momentum of the bullet, (ii) Final momentum of the bullet, (iii) Retardation caused by the wooden block and (iv) Resistive force exerted by the wooden block.
An electron of mass 9 × 10−31 kg is moving with a linear velocity of 6 × 107 ms−1. Calculate the linear momentum of electron.
State two factors which determine the momentum of a body.
What causes motion in a body?
Which of the following has the largest inertia?
State Newton's second law of motion.
A body of mass 400 g is resting on a frictionless table. Find the acceleration of the body when acted upon by a force of 0.02 N.
Use Newton's second law to explain the following:
While catching a fast moving ball, we always pull our hands backwards.
A stone is dropped from a cliff 98 m high.
What will be its speed when it strikes the ground?
A ball is thrown upward and reaches a maximum height of 19.6 m. Find its initial speed?
