Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State Newton's second law of motion.
A body of mass 400 g is resting on a frictionless table. Find the acceleration of the body when acted upon by a force of 0.02 N.
उत्तर
According to Newton's second law of motion, when a force acts on a body, the rate of change in momentum of a body equals the product of the mass of the body and acceleration produced in it due to that force, provided the mass remains constant.
Mass of body = 400 g = 0.4kg
Force applied on body = 0.02 N
Acceleration = force/mass = 0.02/0.4 = 0.05 ms-2.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two bodies of masses 10 kg and 20 kg respectively kept on a smooth, horizontal surface are tied to the ends of a light string. A horizontal force F = 600 N is applied to
- A,
- B along the direction of string. What is the tension in the string in each case?
A free 238U nucleus kept in a train emits an alpha particle. When the train is stationary, a nucleus decays and a passenger measures that the separation between the alpha particle and the recoiling nucleus becomes x at time t after the decay. If the decay takes place while the train is moving at a uniform velocity v, the distance between the alpha particle and the recoiling nucleus at a time t after the decay, as measured by the passenger, is
A force \[\vec{F} = \vec{v} \times \vec{A}\] is exerted on a particle in addition to the force of gravity, where \[\vec{v}\] is the velocity of the particle and \[\vec{A}\] is a constant vector in the horizontal direction. With what minimum speed, a particle of mass m be projected so that it continues to move without being defelected and with a constant velocity?
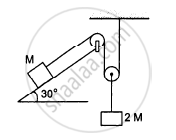
Find the acceleration of the block of mass M in the situation shown in the following figure. All the surfaces are frictionless and the pulleys and the string are light.
Use Newton's second law of motion to explain the following instance :
A cricketer pulls his hands back while catching a fast moving cricket ball .
A force acts for 10 s on a stationary body of mass 100 kg, after which the force ceases to act. The body moves through a distance of 100 m in the next 5 s. Calculate : The magnitude of the force
How long will a stone take to fall to the ground from the top of a building 80 m high
Name the physical quantity which equals the rate of change of linear momentum.
A cricket ball of mass 150 g has an initial velocity `u = (3hati + 4hatj)` m s−1 and a final velocity `v = - (3hati + 4hatj)` m s−1 after being hit. The change in momentum (final momentum-initial momentum) is (in kg m s1)
A hockey player is moving northward and suddenly turns westward with the same speed to avoid an opponent. The force that acts on the player is ______.
