Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
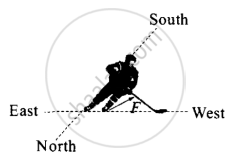
A hockey player is moving northward and suddenly turns westward with the same speed to avoid an opponent. The force that acts on the player is ______.
विकल्प
frictional force along westward.
muscle force along southward.
frictional force along south-west.
muscle force along south-west.
उत्तर
A hockey player is moving northward and suddenly turns westward with the same speed to avoid an opponent. The force that acts on the player is frictional force along south-west.
Explanation:
According to Newton’s second law of motion, only external forces can change the linear momentum of the system. The internal forces cannot change the linear momentum of system under consideration. If we take hockey players as a system, the external force which can change the direction of motion of the player is the force that must be friction between the ground and the shoes of player. The muscle force is the internal force, this cannot change the linear momentum of the player.
According to Newton’s Second Law, The rate of change of linear momentum of a body is equal to the external force applied on the body or F = dp/dt. So, the external force must be in the direction of change in momentum.
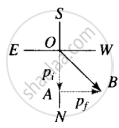
As shown in the diagram,

Let OA = p1
= Initial momentum of player northward
AB = p2
= Final momentum of the player towards west
Clearly OB = OA + AB
According to the problem, mass = 2 kg
The position of the particle is given here as a function of time, x(t) = pt + qt2 + rt3 By differentiating this equation w.r.t. time we get velocity of the particle as a function of time.
v = dx/dt = p + 2 qt + 3 rt2
If we again differentiate this equation w.r.t. time, we will get an acceleration of the particle as a function of time.
a = dv/dt = 0 + 2q + 6rt
At t = 2 s; a = 2q + 6 × 2 × r
= 2 q + 12 r
= 2 × 4 + 12 × 5
= 8 + 60
= 68 m/s
Force = F = ma
= 2 × 68
= 136 N
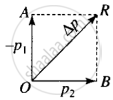
Change in momentum = p2 – p1
= AB – OA
= AB + (– OA)
= Clearly the change in momentum is OR will be along southwest, so the direction of force will also be along southwest.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A person drops a coin. Describe the path of the coin as seen by the person if he is in (a) a car moving at constant velocity and (b) in a free falling elevator.
A car accelerates on a horizontal road due to the force exerted by.
A particle of mass 0.3 kg is subjected to a force F = −kx with k = 15 N/m. What will be its initial acceleration if it is released from a point x = 20 cm?
Suppose the ceiling in the previous problem is that of an elevator which is going up with an acceleration of 2.0 m/s2. Find the elongation.
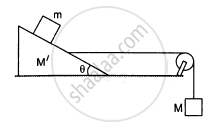
Find the mass M of the hanging block in the following figure that will prevent the smaller block from slipping over the triangular block. All the surfaces are frictionless and the strings and the pulleys are light.
State the Newton's second law of motion. What information do you get from it?
The correct form of Newton's second law is :
Prove mathematically F = ma
What do you mean by linear momentum of a body?
A woman throws an object of mass 500 g with a speed of 25 ms1.
- What is the impulse imparted to the object?
- If the object hits a wall and rebounds with half the original speed, what is the change in momentum of the object?
