Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
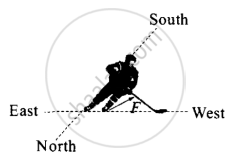
A hockey player is moving northward and suddenly turns westward with the same speed to avoid an opponent. The force that acts on the player is ______.
Options
frictional force along westward.
muscle force along southward.
frictional force along south-west.
muscle force along south-west.
Solution
A hockey player is moving northward and suddenly turns westward with the same speed to avoid an opponent. The force that acts on the player is frictional force along south-west.
Explanation:
According to Newton’s second law of motion, only external forces can change the linear momentum of the system. The internal forces cannot change the linear momentum of system under consideration. If we take hockey players as a system, the external force which can change the direction of motion of the player is the force that must be friction between the ground and the shoes of player. The muscle force is the internal force, this cannot change the linear momentum of the player.
According to Newton’s Second Law, The rate of change of linear momentum of a body is equal to the external force applied on the body or F = dp/dt. So, the external force must be in the direction of change in momentum.
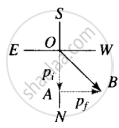
As shown in the diagram,

Let OA = p1
= Initial momentum of player northward
AB = p2
= Final momentum of the player towards west
Clearly OB = OA + AB
According to the problem, mass = 2 kg
The position of the particle is given here as a function of time, x(t) = pt + qt2 + rt3 By differentiating this equation w.r.t. time we get velocity of the particle as a function of time.
v = dx/dt = p + 2 qt + 3 rt2
If we again differentiate this equation w.r.t. time, we will get an acceleration of the particle as a function of time.
a = dv/dt = 0 + 2q + 6rt
At t = 2 s; a = 2q + 6 × 2 × r
= 2 q + 12 r
= 2 × 4 + 12 × 5
= 8 + 60
= 68 m/s
Force = F = ma
= 2 × 68
= 136 N
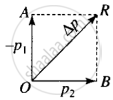
Change in momentum = p2 – p1
= AB – OA
= AB + (– OA)
= Clearly the change in momentum is OR will be along southwest, so the direction of force will also be along southwest.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An aircraft executes a horizontal loop at a speed of 720 km/h with its wings banked at 15°. What is the radius of the loop?
A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination θ. The whole system is accelerated horizontally so that the block does not slip on the wedge. The force exerted by the wedge on the block has a magnitude.
A block of mass 0.2 kg is suspended from the ceiling by a light string. A second block of mass 0.3 kg is suspended from the first block by another string. Find the tensions in the two strings. Take g = 10 m/s2.
Consider the situation shown in the following figure All the surfaces are frictionless and the string and the pulley are light. Find the magnitude of acceleration of the two blocks.

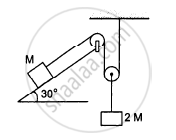
Find the acceleration of the block of mass M in the situation shown in the following figure. All the surfaces are frictionless and the pulleys and the string are light.
Show that the rate of change of momentum = mass × acceleration. Under what condition does this relation hold?
The linear momentum of a ball of mass 50 g is 0.5 kg m s-1. Find its velocity.
A force acts for 10 s on a stationary body of mass 100 kg, after which the force ceases to act. The body moves through a distance of 100 m in the next 5 s. Calculate: The velocity acquired by the body.
Calculate the velocity of a body of mass 0.5 kg, when it has a linear momentum of 5 Ns.
Prove mathematically F = ma
