Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A particle of mass 0.3 kg is subjected to a force F = −kx with k = 15 N/m. What will be its initial acceleration if it is released from a point x = 20 cm?
उत्तर
Displacement of the particle from the mean position, x = 20 cm = 0.2 m
k = 15 N/m
Mass of the particle, m = 0.3 kg
Acceleration, \[a = \frac{\left| F \right|}{m}\]
\[\Rightarrow a = \frac{kx}{m} = \frac{15\left( 0 . 2 \right)}{0 . 3} = \frac{3}{0 . 3} = 10 m/ s^2\]
So, the initial acceleration when the particle is released from a point x = 20 cm is 10 m/s2.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain why a cricketer moves his hands backwards while holding a catch.
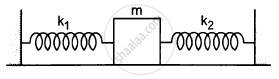
Both the springs shown in the following figure are unstretched. If the block is displaced by a distance x and released, what will be the initial acceleration?
A small block B is placed on another block A of mass 5 kg and length 20 cm. Initially, the block B is near the right end of block A (In the following Figure). A constant horizontal force of 10 N is applied to the block A. All the surfaces are assumed frictionless. Find the time that elapses before block B separates from A.

An empty plastic box of mass m is found to accelerate up at the rate of g/6 when placed deep inside water. How much sand should be put inside the box so that it may accelerate down at the rate of g/6?
Calculate the tension in the string shown in the following figure. The pulley and the string are light and all the surfaces are frictionless. Take g = 10 m/s2.
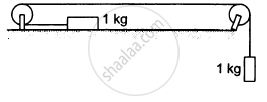
Find the acceleration of the blocks A and B in the three situations shown in the following figure.

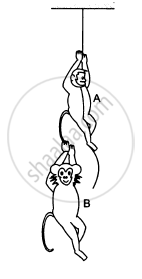
The monkey B, shown in the following figure, is holding on to the tail of monkey A that is climbing up a rope. The masses of monkeys A and B are 5 kg and 2 kg, respectively. If A can tolerate a tension of 30 N in its tail, what force should it apply on the rope in order to carry monkey B with it? Take g = 10 m/s2.
State the Newton's second law of motion. What information do you get from it?
The linear momentum of a body of mass m moving with velocity v is :
Calculate the magnitude of force which when applied on a body of mass 0.5 kg produces an acceleration of 5 m s-2.
A car is moving with a uniform velocity 30 ms-1. It is stopped in 2 s by applying a force of 1500 N through its brakes. Calculate the following values : The change in momentum of car.
A bullet of mass 50 g moving with an initial velocity 100 m s-1 strikes a wooden block and comes to rest after penetrating a distance 2 cm in it. Calculate: (i) Initial momentum of the bullet, (ii) Final momentum of the bullet, (iii) Retardation caused by the wooden block and (iv) Resistive force exerted by the wooden block.
A pebble is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 20 m s-1. How high will it be after 2 s? (Take g = 10 m s-2)
Why is it advantageous to turn before taking a long jump?
Name the physical quantity which equals the rate of change of linear momentum.
What do you mean by an impulsive force?
Use Newton's second law to explain the following:
We always prefer to land on sand instead of hard floor while taking a high jump.
A cricket ball of mass 150 g has an initial velocity `u = (3hati + 4hatj)` m s−1 and a final velocity `v = - (3hati + 4hatj)` m s−1 after being hit. The change in momentum (final momentum-initial momentum) is (in kg m s1)
